At Keentel Engineering, we stay ahead of evolving regulatory frameworks to deliver exceptional power system engineering services. One of the cornerstones of our grid planning expertise lies in our thorough understanding of PJM Manual 14B, which governs the PJM Regional Transmission Expansion Plan (RTEP) — a critical process ensuring grid reliability, economic efficiency, and alignment with public policy objectives across the PJM Interconnection.
With 30+ years of utility-scale experience, our engineers support utilities, IPPs, and developers through each step of PJM regional transmission planning with modeling, compliance, and technical proposal development.
What Is PJM Manual 14B and Why It Matters
PJM Manual 14B outlines the core process for planning transmission system upgrades across the PJM footprint. It includes five key project types:
➤ Baseline Reliability Projects – Required upgrades based on NERC TPL standards.
➤ Supplemental Projects – Driven by Transmission Owners for asset management and local needs.
➤ Market Efficiency Projects – Designed to resolve congestion using a benefit-to-cost ratio.
➤ Public Policy Projects – Support state energy policies via the State Agreement Approach.
➤ Customer-Funded Upgrades – Initiated by interconnection customers or merchant developers.
This planning framework ensures that every project meets FERC, NERC, and state-level energy regulations, while balancing stakeholder input and economic value.
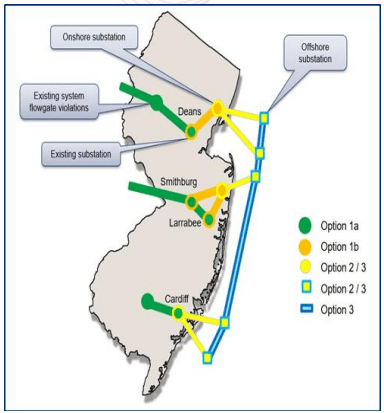
Key Components of the PJM RTEP Process
1. Baseline Reliability Planning
- Identifies and mitigates thermal overloads, voltage violations, and stability issues.
- Relies on load flow, short-circuit, and dynamic modeling over a 15-year planning horizon.
2. Supplemental Projects in PJM
- Initiated by Transmission Owners (TOs) to address asset replacements and lifecycle planning.
- Must pass “do-no-harm” reliability screening before inclusion in the RTEP.
3. Market Efficiency Projects
- Improve cost-efficiency by relieving congestion and lowering production costs.
- Require a 25% minimum benefit-to-cost ratio across 15 years.
4. Public Policy-Driven Planning
- Facilitated through the State Agreement Approach, aligning infrastructure with clean energy mandates.
5. Customer-Funded Transmission Upgrades
- Support interconnections, merchant lines, and special customer-driven capacity additions.
How Keentel Engineering Supports the PJM Transmission Planning Cycle
Keentel Engineering provides full-scope technical, modeling, and regulatory services across all PJM planning categories:
- Power System Studies: Load flow, N-1-1 contingency, stability, and deliverability analysis
- Modeling Support: PSCAD, PSS®E, ASPEN, and ETAP dynamic model development
- PJM Proposal Window Submissions: Economic impact assessments and CEII-ready documentation
- NERC & FERC Compliance: Expertise in TPL, FAC, PRC standards and Form No. 715 requirements
- Asset Retirement & EOL Planning: Evaluating transmission asset end-of-life (EOL) status for reliability impact
Related Services: Learn how our Power System Studies and Substation Design Services support PJM project compliance and system integration.
PJM RTEP FAQs
Q1: What is the PJM RTEP process and why is it important?
The Regional Transmission Expansion Plan (RTEP) identifies necessary transmission upgrades to meet reliability, market, and policy needs across the PJM Interconnection.
Q2: What are Baseline Reliability Projects in PJM?
These are projects required to meet NERC reliability standards, based on PJM’s planning simulations.
Q3: What is a Supplemental Project in PJM Manual 14B?
Projects initiated by Transmission Owners for system maintenance, asset management, or compliance—not necessarily driven by PJM.
Q4: What is “do no harm” evaluation?
A test to ensure proposed upgrades don’t negatively affect the broader grid’s performance or reliability.
Q5: What is the role of FERC Form No. 715?
It outlines local planning criteria, including asset aging and condition-based replacement strategy used in PJM evaluations.
Q6: What software is used in PJM transmission modeling?
PJM primarily uses PSS®E, PowerWorld, and TARA; Keentel adds depth using PSCAD, ASPEN, and ETAP.
Q7: Who can submit proposals during PJM’s planning cycle?
Both incumbent TOs and qualified developers (including merchant providers) may submit projects during PJM’s annual proposal window.
Q8: What is the State Agreement Approach?
A formal method allowing states to sponsor and fund projects that meet local clean energy or climate policy goals.
Q9: How are project costs allocated?
Via PJM’s cost allocation methods, based on whether a project is baseline, supplemental, or market-driven.
Q10: How does Keentel help with PJM submissions?
We support modeling, documentation, proposal justification, CEII data management, and stakeholder presentation preparation.
Why Choose Keentel Engineering for PJM Planning Support?
With decades of experience and deep software proficiency, Keentel delivers:
- Industry-leading PJM RTEP modeling and submittal support
- FERC/NERC compliance alignment for all proposal types
- Technical expertise with modeling tools like PSS®E, PSCAD, ASPEN, ETAP
- Reliable stakeholder representation across TEAC, Subregional RTEP, and FERC dockets
Schedule your RTEP planning consultation today
Email: contact@keentelengineering.com | Call: 813-389-7871
Visit: www.keentelengineering.com