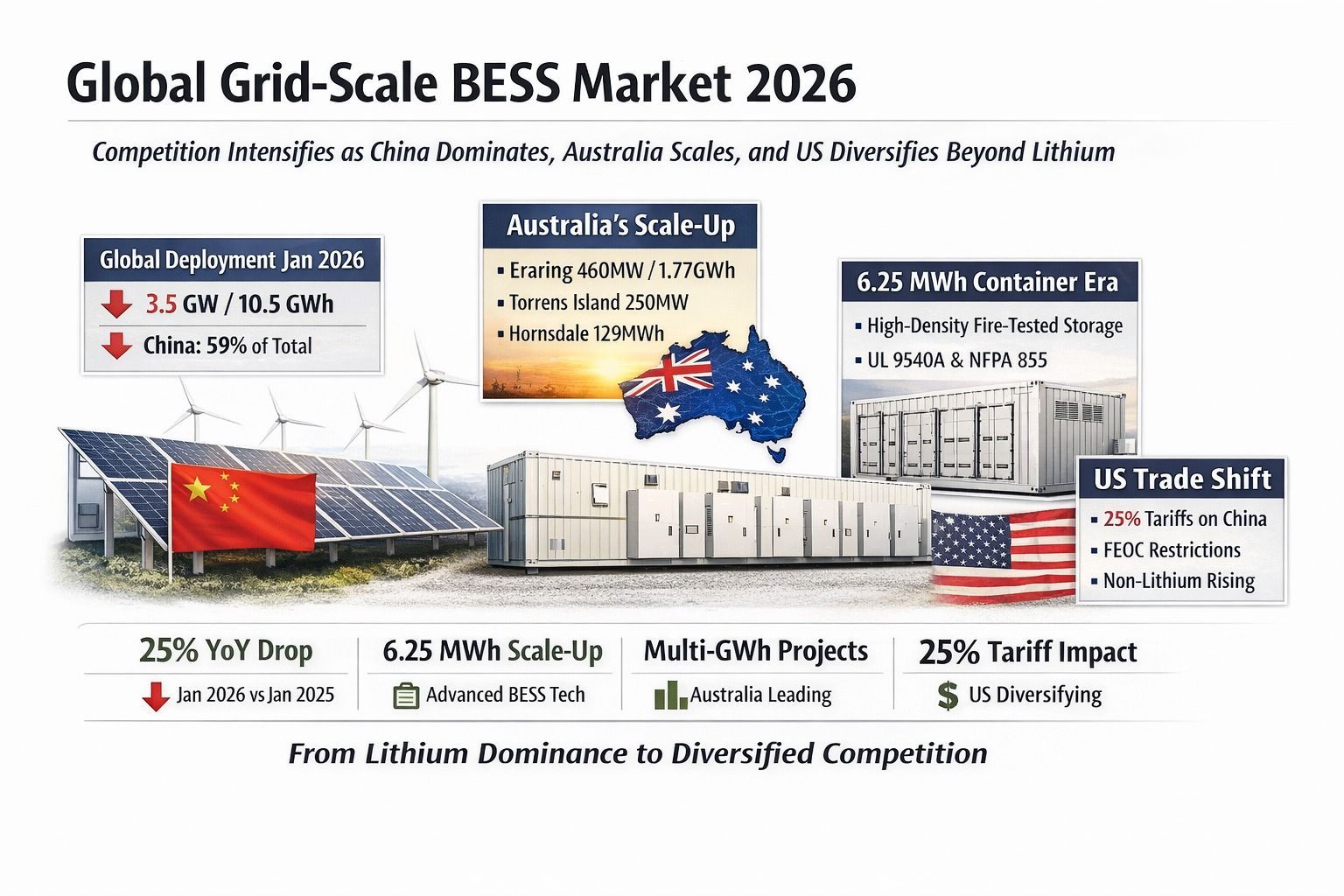
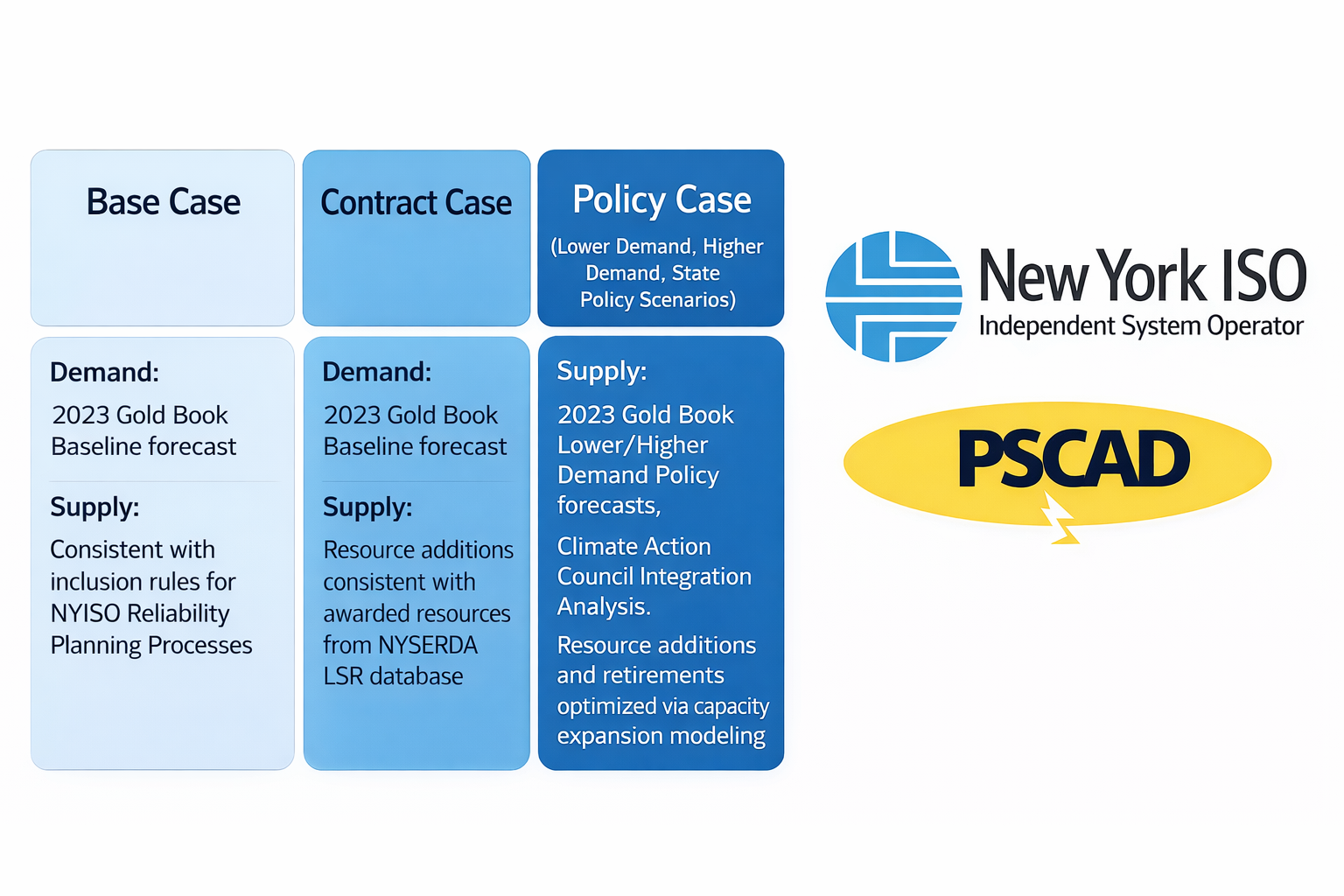
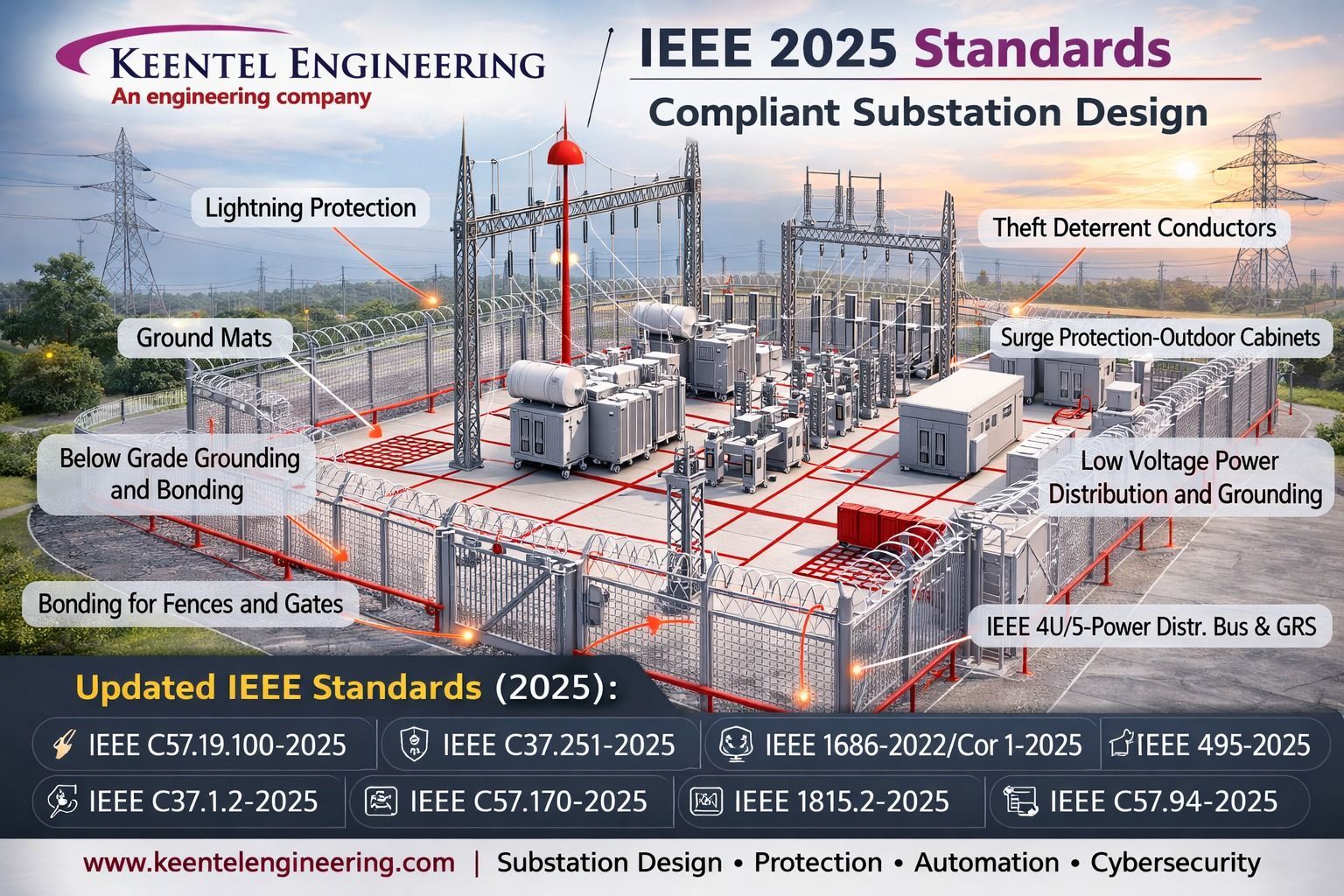
A Coordinated Electric System Interconnection Review—the utility’s deep-dive on technical and cost impacts of your project.
Challenge: Frequent false tripping using conventional electromechanical relays
Solution: SEL-487E integration with multi-terminal differential protection and dynamic inrush restraint
Result: 90% reduction in false trips, saving over $250,000 in downtime
How to Safely Overload Transformers Using IEEE C57.91-2011 Guidelines
April 22, 2025 | Blog
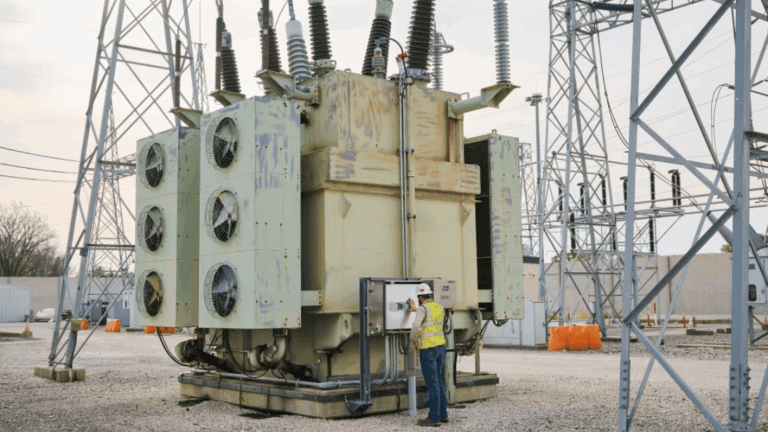

At Keentel Engineering, our commitment to power system reliability and regulatory compliance is backed by decades of transformer analysis expertise. One of the most valuable tools in our transformer engineering arsenal is IEEE Std C57.91-2011, which outlines guidelines for loading mineral-oil-immersed power transformers and step-voltage regulators beyond their nameplate ratings without compromising safety or lifespan.
What Is IEEE C57.91-2011?
IEEE C57.91-2011 is a technical standard published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. It provides detailed thermal performance models and guidelines for planned, emergency, and seasonal overloading of mineral-oil-immersed transformers. The guide explains how transformers rated for 65 °C (and legacy 55 °C systems) can be safely loaded beyond their rated capacity using:
- Hotspot and top-oil temperature rise assessments
- Insulation aging estimation (per-unit life, FAA)
- Risk-based short-term and long-term emergency loading
- Ambient temperature compensation
- Computer-aided loading calculations
Why This Guide Matters
Transformers often experience variable load conditions, especially in renewable integration and substation interconnection projects. Overloading—if executed improperly—can shorten insulation life, create gas evolution from insulating materials, and trigger dielectric breakdowns. IEEE C57.91 provides utilities and engineers with a standardized way to mitigate these risks and maximize transformer usage without compromising safety.
Key Benefits for Utilities and Project Developers
- Quantifiable Risk Management: Through per-unit life and aging acceleration factors, operators can predict insulation aging under elevated temperatures.
- Guided Emergency Planning: The guide supports short-time emergency loading to maintain power during outages or grid instability.
- Customizable Overload Calculations: Adjust loading strategies based on exact transformer parameters (e.g., cooling type, oil volume, top-oil rise, etc.).
- Enhanced Transformer Life Cycle Costing: Balance short-term performance demands with long-term asset health.
Keentel Engineering’s Expertise with IEEE Transformer Loading Guidelines
As industry leaders in Power System Studies and Substation Design, Keentel Engineering integrates IEEE C57.91 into all transformer loading assessments. Our transformer engineering services include:
- Thermal modeling of ONAN and ONAF transformers
- Emergency loading calculations and seasonal strategies
- Life expectancy modeling and insulation degradation curves
- Application of aging acceleration factors (FAA)
- Compliance support for NERC PRC-005 and PRC-019
Whether your project involves a 20 MVA substation bank or small distribution regulators, we apply these guidelines for safe, cost-effective transformer operation—especially during variable or peak load conditions.
Top Questions Answered
What does IEEE C57.91-2011 cover?
It provides loading recommendations for mineral-oil-immersed transformers and step-voltage regulators, including risk assessment during overload conditions.
What is the significance of 65 °C winding rise?
This is the standard temperature rating for modern transformer insulation systems, determining the basis for thermal aging and loading capacity.
Can I load my transformer above its nameplate?
Yes, under the guidelines, controlled overloading is permissible with consideration for insulation aging, ambient temperature, and cooling design.
What are aging acceleration factors (FAA)?
These indicate how much faster insulation ages at various hotspot temperatures compared to the baseline 110 °C.
What is per-unit insulation life?
It’s the ratio of expected insulation life at a given temperature to that at the standard 110 °C, allowing lifespan estimates.
How is top-oil rise calculated?
It uses exponential models considering oil cooling time constants and initial vs. ultimate oil temperatures.
What’s the role of ambient temperature?
Ambient conditions significantly influence allowable overload limits and insulation degradation rates.
Can this guide be applied to step-voltage regulators?
Yes, dedicated sections and formulas are provided for assessing regulator loading.
How does overload impact transformer bushings and tap changers?
Excessive currents can increase thermal stress and gas evolution, risking mechanical failure.
What are short-time and long-time emergency loading?
Short-time refers to overloads lasting minutes to hours; long-time spans several hours to days. Each has defined thermal and insulation impacts.
Is this guide applicable to 55 °C systems?
Yes, it includes recommendations for legacy systems with 55 °C average winding temperature rise.
What data is needed for accurate calculations?
Load losses, oil weights, insulation details, temperature rise tests, and oil flow type (directed vs. non-directed).
Can I use this guide without a computer?
Basic loading approximations are possible manually, but detailed evaluation is best done with modeling software.
What is cold-load pickup (CLPU)?
It’s the sudden, high inrush current when loads are restored after an outage, covered in Annex F.
How does insulation aging relate to transformer life?
While insulation life is a key factor, transformer life may exceed it depending on mechanical wear and maintenance.
Are there differences in loading power vs. distribution transformers?
Yes, the guide provides specific limits and risk factors based on transformer size and voltage class.
What is the loss of life percentage?
It quantifies the insulation lifespan used during a given overload cycle—important for asset management.
How does altitude or temperature affect transformer loading?
High altitudes and extreme ambient temperatures reduce cooling efficiency and loading capacity.
What’s the difference between ONAN and ONAF cooling?
ONAN is natural air cooling; ONAF adds forced air (fans), increasing load capability.
How can Keentel Engineering help?
We offer complete transformer study packages, integrating IEEE C57.91 into practical solutions aligned with utility needs and grid codes.
Related Services You Might Need
Explore our full range of engineering services that complement transformer performance planning:
Final Takeaway
Transformer overloading isn’t just about pushing limits—it’s about understanding them. At Keentel Engineering, we help utilities, IPPs, and project developers implement the IEEE C57.91-2011 guide into practical, reliable, and risk-adjusted transformer operations. Whether you’re managing 24/7 industrial loads or dynamic solar interconnections, we deliver customized insights backed by standards-based modeling.
Ready to Optimize Transformer Reliability?
Contact Keentel Engineering today to explore how IEEE C57.91-2011 transformer loading guidance can reduce your O&M risk and maximize performance across utility and industrial power systems.

About the Author:
Sonny Patel P.E. EC
IEEE Senior Member
In 1995, Sandip (Sonny) R. Patel earned his Electrical Engineering degree from the University of Illinois, specializing in Electrical Engineering . But degrees don’t build legacies—action does. For three decades, he’s been shaping the future of engineering, not just as a licensed Professional Engineer across multiple states (Florida, California, New York, West Virginia, and Minnesota), but as a doer. A builder. A leader. Not just an engineer. A Licensed Electrical Contractor in Florida with an Unlimited EC license. Not just an executive. The founder and CEO of KEENTEL LLC—where expertise meets execution. Three decades. Multiple states. Endless impact.
Services

Let's Discuss Your Project
Let's book a call to discuss your electrical engineering project that we can help you with.

About the Author:
Sonny Patel P.E. EC
IEEE Senior Member
In 1995, Sandip (Sonny) R. Patel earned his Electrical Engineering degree from the University of Illinois, specializing in Electrical Engineering . But degrees don’t build legacies—action does. For three decades, he’s been shaping the future of engineering, not just as a licensed Professional Engineer across multiple states (Florida, California, New York, West Virginia, and Minnesota), but as a doer. A builder. A leader. Not just an engineer. A Licensed Electrical Contractor in Florida with an Unlimited EC license. Not just an executive. The founder and CEO of KEENTEL LLC—where expertise meets execution. Three decades. Multiple states. Endless impact.
Leave a Comment
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.
Related Posts