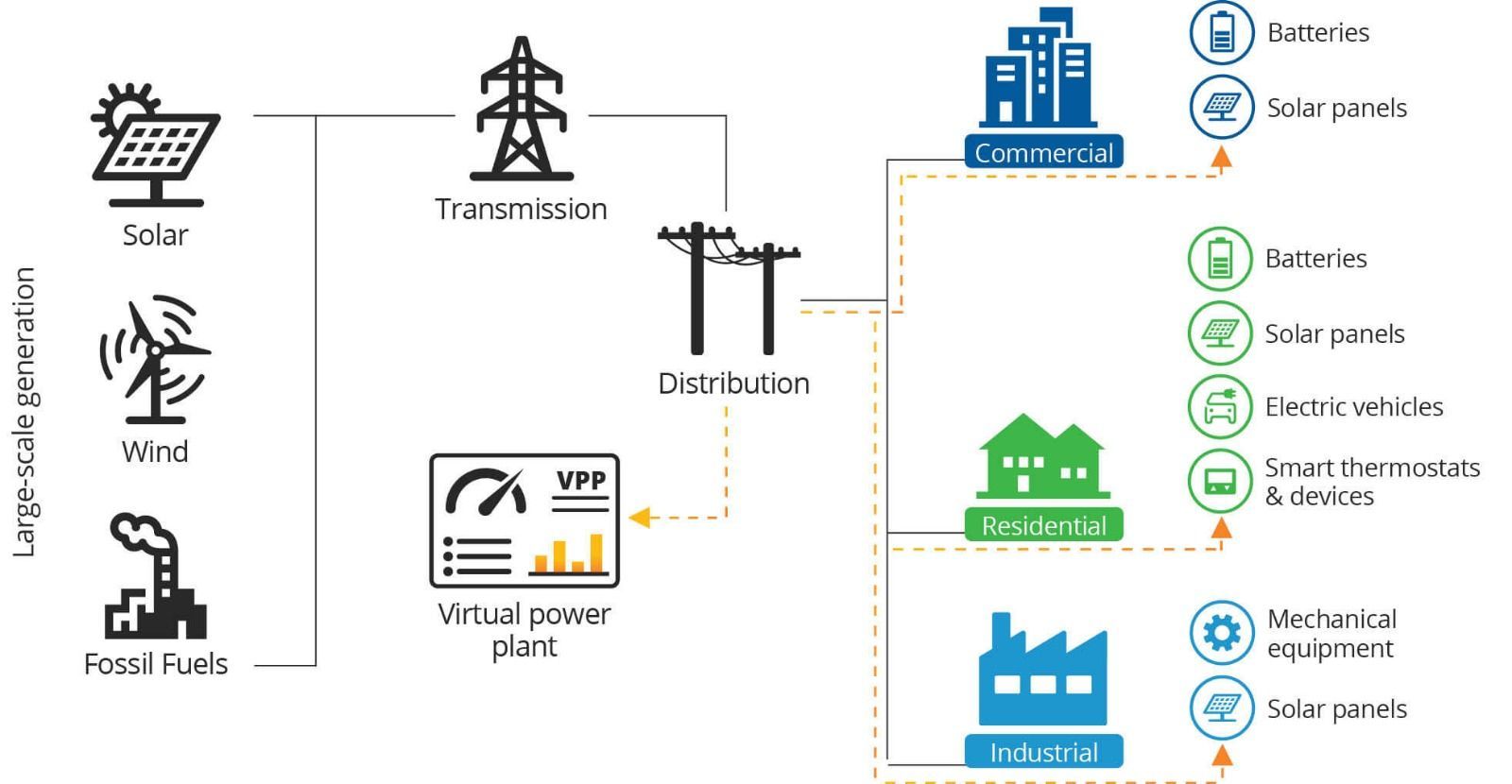
A Coordinated Electric System Interconnection Review—the utility’s deep-dive on technical and cost impacts of your project.
Keentel Engineering Insights: NERC Identifies New Grid Vulnerabilities – May 2025 Newsletter
May 9, 2025 | Blog

By: Keentel Communications Team
Newsletter: May 2025
NERC Issues Critical Grid Vulnerability Alert in Latest Canadian Transmission Assessment
Keentel Engineering is closely tracking the latest developments from the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC), which recently released the Canadian segment of its Interregional Transfer Capability Study (ITCS). The April 29 announcement underscores a growing vulnerability in Canada’s electric grid, highlighting both the strain of extreme weather and the limited interprovincial transfer capacity.
The ITCS Canadian Analysis builds upon last year’s U.S.-focused assessment to provide a comprehensive, continent-wide picture of grid resilience and interdependence. According to NERC’s CEO Jim Robb, the findings reflect “an unprecedented and vital assessment” with a focus on the need for strengthened cross-border and cross-provincial transmission infrastructure.
“This analysis shows where targeted improvements to transmission infrastructure could further leverage Canada’s significant generation resources to support reliability and resilience across the North American bulk power system.”
— John Moura, Director of Reliability Assessments, NER
Key Findings of the Canadian Analysis
Increased Vulnerability
Every one of the 12 weather years analyzed indicated potential for energy inadequacy, especially under extreme conditions.
Insufficient Interprovincial Transfer Capability
Higher transfer capability exists between Canada and the U.S. than between Canadian provinces.
Need for Infrastructure Investment
Enhancing transfer interfaces by 12–14 GW could help reduce risk during grid stress events.
Regional Customization Required
Solutions must be tailored to provincial needs, considering weather variability, local risks, and energy policies.
Strategic Grid Planning Emphasized
NERC calls for interregional collaboration and long-term planning amid ongoing electrification trends.
These findings reinforce the urgent need for resilient grid architecture that can handle rising energy demands from sectors like transportation, data centers, and industry, especially as the climate changes.
New Standards, Compliance, and Enforcement Updates: May 2025 Highlights
In parallel, NERC released its Standards, Compliance, and Enforcement Bulletin for the week of May 5–11, 2025, providing vital information on standards activity that could affect generator operators, transmission planners, and system reliability stakeholders.
Active Ballots and Comment Periods
- Project 2024-01 – Rules of Procedure Definitions Alignment (GO and GOP)
Ballot ends: May 7, 2025
Focuses on aligning terms used by Generator Owners and Operators. - Project 2020-06 – Verification of Models and Data for Generators
Ballot ends: May 12, 2025
Enhances standards surrounding model/data validation critical for system simulations. - Project 2022-02 & 2021-01 – Inverter-Based Resource (IBR) Framework and Model Validation
Aimed at improving the performance and integration of IBRs.
New Initiatives
- Project 2023-09 explores risk management for third-party cloud services.
- Project 2023-08 is currently accepting nominations for drafting team members focusing on MOD-031 updates for energy and demand data.
System Maintenance Alert
Planned downtime for the Align system is scheduled for May 10–11, affecting compliance reporting access.
Implications for Keentel and the Broader Industry
These updates are especially relevant as Keentel Engineering continues to support utilities and infrastructure developers with state-of-the-art compliance solutions, engineering design, and resilience planning. The insights from NERC underscore both the technical and policy challenges that lie ahead—and the opportunity for forward-looking firms to lead.
As industry expectations shift toward integrated, cross-border grid strategies and robust compliance systems, Keentel is committed to aligning with the latest standards and contributing to a secure energy future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the NERC ITCS Canadian Analysis?
The Interregional Transfer Capability Study (ITCS) Canadian Analysis, released by NERC on April 29, 2025, assesses the ability of Canadian power systems to transfer electricity across provincial and international borders. It highlights vulnerabilities in Canada’s grid under extreme weather and recommends enhancing transmission infrastructure to support resilience.
2. Why is this study important to grid reliability?
The study shows that Canada’s bulk power system is increasingly vulnerable due to limited interprovincial transmission capacity and growing extreme weather events. Improved transfer capability could reduce the likelihood of power deficits during grid stress events.
3. What does this mean for the U.S.-Canada electric relationship?
It reinforces that the U.S. and Canadian grids are highly interdependent. Strengthening transmission infrastructure between regions can boost shared reliability and support load balancing during high-demand or emergency scenarios.
TECHNICAL FINDINGS
4. What are the key findings from the Canadian Analysis?
- High U.S.-Canada transfer potential, but low interprovincial connectivity.
- 12–14 GW of additional capacity could mitigate extreme weather-related risks.
- Regional weather drives localized vulnerability.
- Ontario and Québec show resource growth aligning with forecasted demand.
- A mix of local generation, storage, and demand-side solutions is needed.
5. What role do weather and demand forecasting play?
Regional weather greatly influences risk. Updated long-term reliability forecasts (especially in Ontario and Québec) have narrowed the gap between supply and demand. However, ongoing updates are essential as electrification expands.
STANDARDS AND COMPLIANCE UPDATES
6. What new NERC standards activities are underway?
Several projects are active, including:
- 2024-01: Rules of Procedure Definitions Alignment (GO/GOP)
- 2020-06: Verification of Generator Models/Data
- 2022-02 & 2021-01: IBR framework and model validation
Ballot and comment periods run throughout May 2025.
7. What is Project 2023-09 and why is it notable?
Project 2023-09 addresses risk management for third-party cloud services, a growing concern as utilities digitize operations. It introduces standards for secure cloud infrastructure in the power sector.
8. Are there changes to upcoming standards enforcement dates?
Yes. New and revised standards will take effect through 2027. Notable examples:
- IRO-010-5 and TOP-003-6.1 – July 1, 2025
- CIP-003-9 (Cybersecurity) – April 1, 2026
- TPL-008-1 (Extreme Temperature Planning) – April 1, 2026
U.S. Effective Dates for Reliability Standards
| U.S. Effective Date | Standard(s) | Phased-In (Y/N) |
|---|---|---|
| July 1, 2025 | IRO-010-5-Reliability Coordinator Data and information Specification and Collection | Implementation Plan | No |
| July 1, 2025 | TOP-003-6.1-Transmission Operator and Balancing Authority Data and Information Specification and Collection Implementation Plan | No |
| October 1, 2025 | TOP-002-5-Operations Planning | Implementation Plan | No |
| April 1, 2026 | CIP-003-9- Cyber Security Security Management Controls | Implementation Plan | No |
| April 1, 2026 | TPL-008-1-Transmission System Planning Performance Requirements for Extreme Temperature Events | Implementation Plan | Yes |
| July 1, 2026 | CIP-012-2-Cyber Security-Communications between Control Centers | Implementation Pian | No |
| October 1. 2026 | TOP-003-7-Transmission Operator and Balancing Authority Data and Information Specification and Collection Implementation Plan | No |
| April 1, 2027 | BAL-007-1-Near-term Energy Reliability Assessments | Implementation Plan | No |
MPLICATIONS FOR STAKEHOLDERS
9. What does this mean for utilities and operators?
Organizations must prepare for both climate-driven reliability risks and increasing compliance complexity. Enhanced modeling, planning, and resource diversity are critical to meet evolving reliability requirements.
10. How is Keentel Engineering responding?
Keentel is proactively adapting to these insights by:
- Supporting clients with enhanced modeling and forecasting services.
- Preparing for new compliance enforcement timelines.
- Advising on interregional planning and infrastructure strategies.
LOOKING AHEAD
11. What’s next on the regulatory horizon?
More grid planning and compliance activities are expected in response to:
- Extreme weather preparedness
- Electrification trends
- Cybersecurity risk (CIP standards)
- Infrastructure modernization (IBR, cloud risk, etc.)
12. Where can I get more information?
For full reports and project details:
You can also contact Keentel’s compliance team for tailored guidance.
For detailed guidance on integrating these insights into your projects, contact our compliance team at contact@keentelengineering.com or visit our NERC compliance page.

About the Author:
Sonny Patel P.E. EC
IEEE Senior Member
In 1995, Sandip (Sonny) R. Patel earned his Electrical Engineering degree from the University of Illinois, specializing in Electrical Engineering . But degrees don’t build legacies—action does. For three decades, he’s been shaping the future of engineering, not just as a licensed Professional Engineer across multiple states (Florida, California, New York, West Virginia, and Minnesota), but as a doer. A builder. A leader. Not just an engineer. A Licensed Electrical Contractor in Florida with an Unlimited EC license. Not just an executive. The founder and CEO of KEENTEL LLC—where expertise meets execution. Three decades. Multiple states. Endless impact.
Services

Let's Discuss Your Project
Let's book a call to discuss your electrical engineering project that we can help you with.

About the Author:
Sonny Patel P.E. EC
IEEE Senior Member
In 1995, Sandip (Sonny) R. Patel earned his Electrical Engineering degree from the University of Illinois, specializing in Electrical Engineering . But degrees don’t build legacies—action does. For three decades, he’s been shaping the future of engineering, not just as a licensed Professional Engineer across multiple states (Florida, California, New York, West Virginia, and Minnesota), but as a doer. A builder. A leader. Not just an engineer. A Licensed Electrical Contractor in Florida with an Unlimited EC license. Not just an executive. The founder and CEO of KEENTEL LLC—where expertise meets execution. Three decades. Multiple states. Endless impact.
Leave a Comment
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.