A Coordinated Electric System Interconnection Review—the utility’s deep-dive on technical and cost impacts of your project.
Challenge: Frequent false tripping using conventional electromechanical relays
Solution: SEL-487E integration with multi-terminal differential protection and dynamic inrush restraint
Result: 90% reduction in false trips, saving over $250,000 in downtime
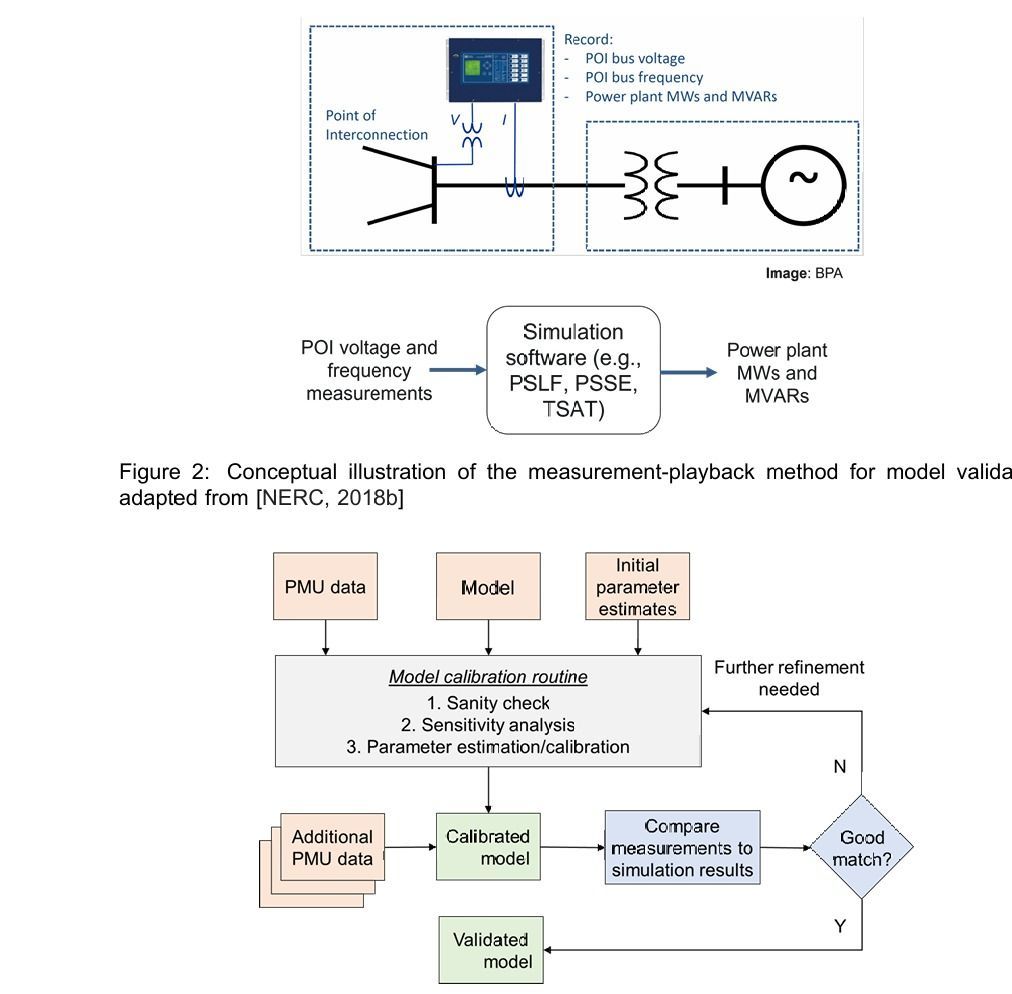
NERC MOD-033-1 Steady-State & Dynamic Model Validation
September 13, 2025 | Blog
Introduction
Reliable electric power systems depend on accurate models that represent real-world grid behavior. Inaccurate models can lead to flawed planning studies, missed risks, and even system instability. To address this, the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) developed MOD-033-1: Steady-State and Dynamic System Model Validation, a standard designed to ensure that system models are consistently validated against actual operating data mod-033-1.
This standard complements MOD-032-1, which governs the collection of modeling data. While MOD-032-1 ensures data is submitted by applicable entities, MOD-033-1 focuses on verifying the accuracy of those models through periodic validation exercises.
Purpose of MOD-033-1
The primary goal is to establish consistent validation requirements for both steady-state (power flow) and dynamic (system response) models. By comparing simulations with real-world data, planning coordinators and reliability entities can identify gaps, improve accuracy, and strengthen grid reliability
mod-033-1.
This aligns with the broader expectation under the nerc mod-033-1 steady-state and dynamic system model validation framework, where model performance must consistently match actual system behavior.
Learn about: Power system modeling services
Many planners also look for technical guidance related to pscad model validation nerc, especially when validating inverter-based resources or dynamic models using EMT-based tools.
Applicability
MOD-033-1 applies to:
- Planning Coordinators (responsible for overseeing planning areas),
- Reliability Coordinators, and
- Transmission Operators.
These entities must collaborate to ensure the accuracy of power flow and dynamics models across interconnected transmission systems mod-033-1.These responsibilities are defined within the nerc functional model, which outlines how different entities coordinate model development and validation.
Core Requirements
1. Documented Validation Process (R1)
Each Planning Coordinator must create and implement a validation process that includes:
- Steady-State Validation: Comparing planning power flow models against actual system behavior (e.g., state estimator cases or real-time data) at least once every 24 months.
- Dynamic Validation: Comparing dynamic models with system responses to local dynamic events (e.g., line switching near a generator, localized oscillations) at least once every 24 months.
- Guidelines for Acceptable Differences: Defining what constitutes unacceptable discrepancies between modeled and actual performance.
- Resolution Process: Documenting how identified discrepancies will be resolved mod-033-1.
For many entities, the first step is validation, ensuring that models and actual system responses align before deeper analysis is performed.
2. Data Sharing Requirement (R2)
Reliability Coordinators and Transmission Operators must provide actual system data to Planning Coordinators within 30 days of a request. This includes disturbance data, state estimator cases, or other real-time measurements.
Compliance and Enforcement
Entities must retain evidence of validation and data-sharing practices from the last audit cycle. Violation Severity Levels (VSLs) range from Lower (minor delays in validation) to Severe (failure to maintain or document any validation process).
For example, the
compliance table on page 5 outlines severity levels based on how late or incomplete a validation is, with Severe VSL covering cases where no validation occurs at all mod-033-1.
Guidelines and Technical Basis
The standard allows flexibility in methodology but requires meaningful comparisons. Examples include:
- Voltage levels at major buses,
- Load distribution and load power factors,
- Power flows on key transmission lines,
- Oscillation patterns during disturbances.
These validation steps ensure that planners can accurately assess real-time system behavior and identify gaps before they become reliability risks. For deeper context on why dynamic modeling is critical, explore the importance of dynamic models for grid reliability.
Dynamic event comparison often rely on visual inspection of plot, frequency excursion, or transient rise times. Planning Coordinators are expected to define thresholds suitable for their systems mod-033-1.
In some cases, mod 33 is referenced informally to describe these validation expectations within planning studies.
Rationale
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) directed NERC to establish validation standards (Order No. 693). MOD-033-1 fulfills that directive by ensuring models reflect actual system performance. This alignment improves the accuracy of:
- Power flow studies,
- Voltage and frequency analysis,
- Dynamic stability assessments mod-033-1.
These assessments often use principles from dynamical systems modeling, especially when evaluating how the system responds to disturbances.
Benefits of MOD-033-1
- Improved Model Accuracy: Reduces discrepancies between studies and actual operations.
- Enhanced Reliability: Ensures planners and operators have dependable tools.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meets FERC directives and NERC mandates.
- Data-Driven Improvements: Encourages collaboration between coordinators, transmission operators, and reliability coordinators.
Learn more: Synchrophasor (PMU) technology for real-time grid monitoring
Conclusions
Electromagnetic transient (EMT) analysis is no longer optional — it is foundational for maintaining grid NERC MOD-033-1 plays a critical role in bridging the gap between theoretical planning models and the real-world behavior of the power grid. By requiring systematic validation of both steady-state and dynamic system models, the standard ensures that simulations are not only technically sound but also operationally reliable. This helps Planning Coordinators, Reliability Coordinators, and Transmission Operators detect discrepancies early, improve the accuracy of studies, and maintain compliance with regulatory expectations.
Ultimately, MOD-033-1 strengthens the resilience of the interconnected grid by making sure that planning tools reflect actual system conditions. For utilities and operators, this means fewer surprises during disturbances, more dependable expansion planning, and a higher level of confidence in critical decision-making. In an era of increasing grid complexity and renewable integration, model validation under MOD-033-1 is not just a compliance obligation—it is a cornerstone of reliable and secure power system operation.
Frequently Asked Questions – EMT Analysis
1. What is the purpose of MOD-033-1?
To ensure planning models for steady-state and dynamic simulations accurately reflect real-world system behavior through regular validation.
2. Who must comply with MOD-033-1?
Planning Coordinators, Reliability Coordinators, and Transmission Operators.
3. How often must validation occur?
At least once every 24 months for both steady-state and dynamic models.
4. What is considered a “dynamic local event”?
A disturbance producing measurable oscillations or transient responses localized to a system area (e.g., switching a transmission line near a generator).
5. What happens if no local event occurs within 24 months?
The next available dynamic local event must be used, even if it occurs later.
6. What data sources are acceptable for validation?
State estimator cases, disturbance recordings, and other real-time measurement data.
7. How are discrepancies handled?
Planning Coordinators must establish guidelines to determine unacceptable differences and a process to resolve them.
8. What is Requirement R2 about?
It requires Reliability Coordinators and Transmission Operators to provide requested system behavior data within 30 days.
9. What evidence must entities keep?
Records of validation processes, simulations, and data exchanges since the last audit.
10. What are Violation Severity Levels (VSLs)?
They range from Lower (minor delays or missing one element) to Severe (no validation process or complete failure to comply).
11. Why is validation important for reliability?
It ensures planning studies align with real-world system behavior, reducing risks of instability or misoperation.
12. How does MOD-033-1 differ from MOD-032-1?
MOD-032-1 governs data collection, while MOD-033-1 governs data validation.
13. Who enforces compliance?
NERC and its Regional Entities.
14. How long must evidence be retained?
Since the last audit, unless otherwise directed by the Compliance Enforcement Authority.
15. Can Planning Coordinators choose their own validation methods?
Yes, but they must include guidelines for determining and resolving unacceptable differences.
16. What tools are typically used for validation?
Simulation software, phasor measurement units (PMUs), state estimators, and disturbance recorders.
17. How does this improve transmission planning?
It aligns simulations with reality, enabling more reliable grid expansion and operational planning.
18. What happens if discrepancies cannot be resolved locally?
They should be reported to the Electric Reliability Organization (ERO).
19. Does this apply Interconnection-wide?
No, validation focuses on the Planning Coordinator’s area, while Interconnection-wide studies are handled separately by the ERO.
20. When did MOD-033-1 become effective?
It became effective 36 months after approval by the applicable governmental authority (FERC approved it on May 1, 2014).
EMT Analysis in the Context of MOD-033-1
While NERC MOD-033-1 focuses on validating steady-state and dynamic models against real-world operating data, many modern systems now require an additional layer of analysis: electromagnetic transient (EMT) simulations. This is especially true as inverter-based resources (IBRs) such as solar, wind, and battery energy storage introduce high-speed switching dynamics and control interactions that traditional RMS tools cannot fully capture.
Why EMT Complements MOD-033-1 Validation
- Captures fast transients that affect reliability but are invisible to power-flow or RMS stability models.
- Ensures accurate protection coordination, reducing the risk of relay misoperations.
- Supports regulatory expectations, including NERC PRC and IEEE standards for IBR performance.
- Strengthens weak-grid studies, black-start planning, and integration of FACTS devices.
Keentel Engineering’s EMT Expertise
To support utilities, planning coordinators, and developers in meeting both compliance and reliability goals, Keentel Engineering provides:
- Detailed EMT models for solar, wind, HVDC, and BESS systems.
- Co-simulation with RMS tools (PSS®E, DIgSILENT, PSCAD) for full-spectrum model validation.
- Real-time and HIL testing to verify dynamic performance and ride-through capability.
- System-wide studies addressing hidden risks in weak grids and restoration scenarios.
By combining MOD-033-1 validation requirements with advanced EMT analysis, we help stakeholders future-proof their transmission planning and operations. This ensures that models not only pass regulatory audits but also reflect the true performance of today’s increasingly complex power systems.

About the Author:
Sonny Patel P.E. EC
IEEE Senior Member
In 1995, Sandip (Sonny) R. Patel earned his Electrical Engineering degree from the University of Illinois, specializing in Electrical Engineering . But degrees don’t build legacies—action does. For three decades, he’s been shaping the future of engineering, not just as a licensed Professional Engineer across multiple states (Florida, California, New York, West Virginia, and Minnesota), but as a doer. A builder. A leader. Not just an engineer. A Licensed Electrical Contractor in Florida with an Unlimited EC license. Not just an executive. The founder and CEO of KEENTEL LLC—where expertise meets execution. Three decades. Multiple states. Endless impact.
Services

Let's Discuss Your Project
Let's book a call to discuss your electrical engineering project that we can help you with.

About the Author:
Sonny Patel P.E. EC
IEEE Senior Member
In 1995, Sandip (Sonny) R. Patel earned his Electrical Engineering degree from the University of Illinois, specializing in Electrical Engineering . But degrees don’t build legacies—action does. For three decades, he’s been shaping the future of engineering, not just as a licensed Professional Engineer across multiple states (Florida, California, New York, West Virginia, and Minnesota), but as a doer. A builder. A leader. Not just an engineer. A Licensed Electrical Contractor in Florida with an Unlimited EC license. Not just an executive. The founder and CEO of KEENTEL LLC—where expertise meets execution. Three decades. Multiple states. Endless impact.
Leave a Comment
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.