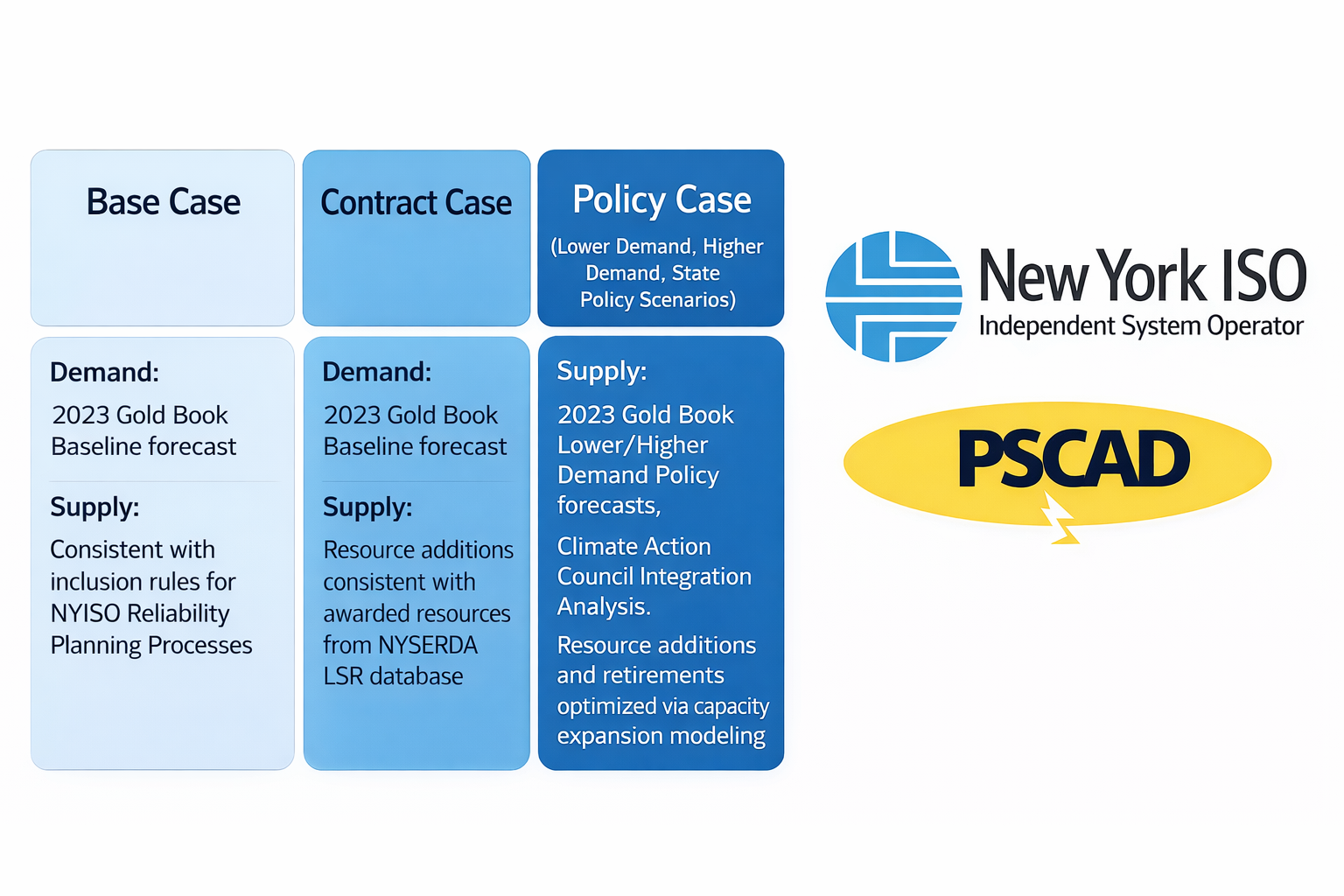
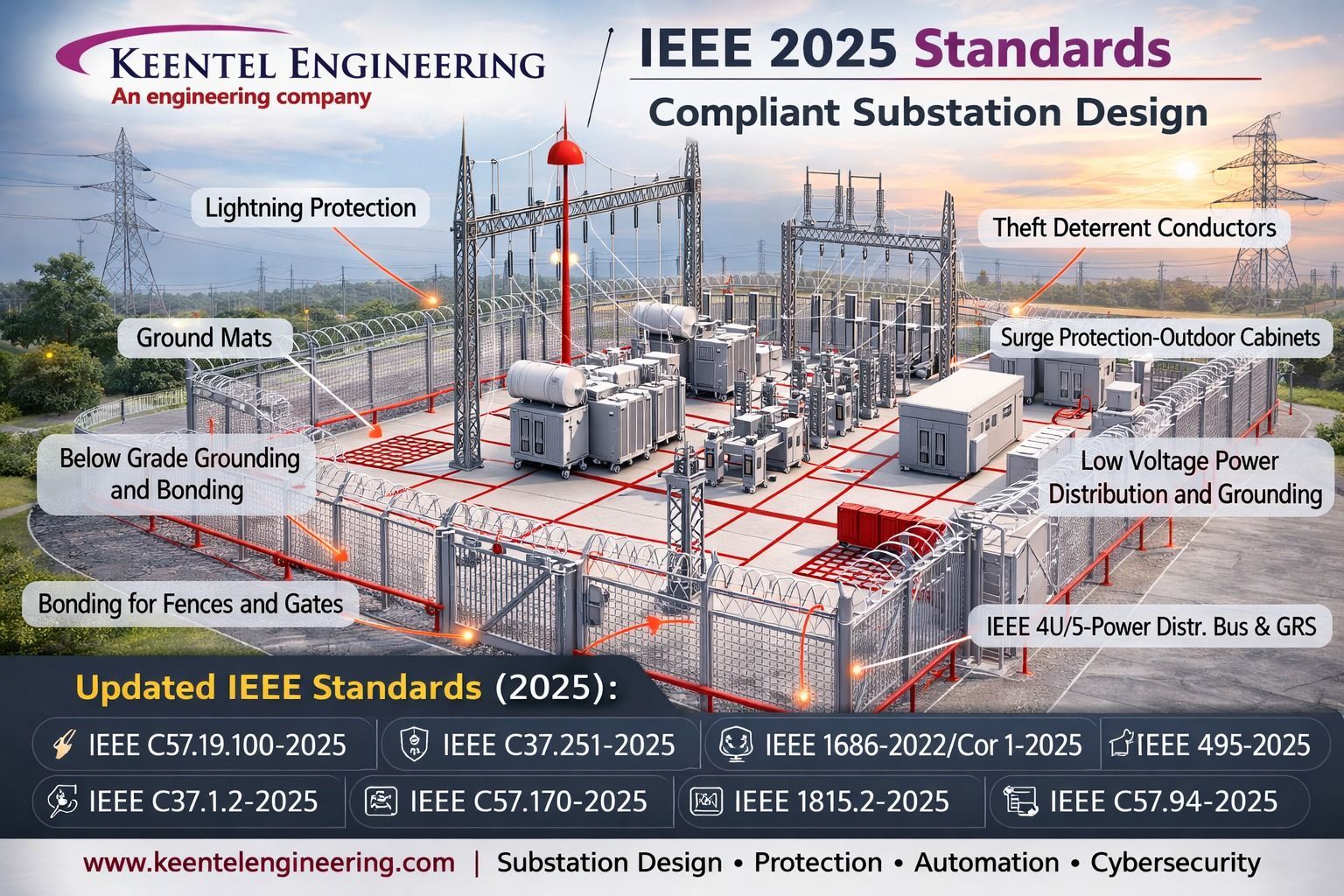
A Coordinated Electric System Interconnection Review—the utility’s deep-dive on technical and cost impacts of your project.
Challenge: Frequent false tripping using conventional electromechanical relays
Solution: SEL-487E integration with multi-terminal differential protection and dynamic inrush restraint
Result: 90% reduction in false trips, saving over $250,000 in downtime
What Is the Difference Between FERC and NERC?
November 23, 2024|Blog

In the complex field of power and utility systems, two primary regulatory bodies shape the operations and policies of the electric grid in North America: the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) and the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC). While both organizations share a commitment to reliability and safety in the power industry, their roles, responsibilities, and operational focuses differ significantly.
Understanding FERC: The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission
FERC is an independent U.S. federal agency that regulates the interstate transmission of electricity, natural gas, and oil. Established under the Department of Energy Organization Act of 1977, FERC’s primary mission is to ensure that energy markets operate fairly and reliably, with a focus on public and environmental safety.
Key Responsibilities of FERC
FERC’s authority extends across multiple aspects of the energy industry, particularly focusing on:
- Electricity Transmission and Wholesale Rates: FERC oversees the interstate transmission of electricity and regulates wholesale electricity rates, ensuring fair pricing across state lines.
- Natural Gas Pipelines and Storage: FERC licenses interstate natural gas pipeline construction, storage, and transport facilities.
- Hydroelectric Licensing: FERC is also responsible for licensing non-federal hydroelectric power projects and assessing their environmental impact.
FERC’s Role in Market Integrity and Competition
FERC fosters a competitive, reliable, and efficient energy market. By regulating rates, tariffs, and market operations, FERC seeks to prevent market manipulation and ensure consumer access to fair and just energy pricing.
Regulatory Enforcement and Compliance
FERC enforces energy regulations by imposing penalties on entities that fail to comply with market standards. It actively investigates and addresses instances of non-compliance to maintain market integrity.
Unpacking NERC: The North American Electric Reliability Corporation
NERC, a nonprofit organization, ensures the reliability and security of the bulk power system in North America. Its primary goal is to develop and enforce reliability standards that prevent widespread outages, focusing on operational stability and planning.
NERC’s Core Mission and Functions
NERC’s mission is centered on the reliability of the bulk electric system. It achieves this by:
- Developing Reliability Standards: NERC creates and enforces a set of operational and planning standards designed to ensure the electric grid’s resilience. These standards include essential guidelines on system monitoring, control, and communication protocols.
- Compliance Monitoring and Enforcement: NERC regularly audits power companies and utilities to ensure they meet established standards, fostering accountability across the industry.
- Event Analysis and Training: NERC analyzes grid disturbances to derive lessons and improve future operations. It also provides training and educational resources to help industry professionals understand and adhere to these standards.
The Importance of NERC’s Operation and Planning Standards
The standards NERC sets are vital for:
- Reliability: Ensuring a reliable electricity supply across North America, particularly during peak demand times.
- Coordination: Promoting coordination among various power entities, enhancing communication and efficiency within the grid.
- Regulatory Compliance: Enforcing standards compliance helps utilities avoid penalties and reinforces the grid’s operational integrity.
FERC vs. NERC: Key Differences
Though both FERC and NERC aim to safeguard the stability of the energy grid, they have distinct areas of focus and authority.
Jurisdiction and Authority
- FERC: A government body with authority over interstate energy transactions, FERC is a U.S. federal agency that enforces laws governing electricity and natural gas rates, interstate energy transport, and market practices.
- NERC: Operating as a regulatory authority under FERC’s jurisdiction, NERC is a nonprofit corporation responsible for developing reliability standards for the bulk power system, which extends across North America, including parts of Canada and Mexico.
Primary Focus Areas
- FERC: Concentrates on fair market practices, pricing, and licensing, with a broader focus on regulating the entire energy market in the United States.
- NERC: Focuses solely on reliability standards and the operational and planning aspects of grid stability, particularly within the bulk power system.
Enforcement and Compliance
- FERC: Enforces energy market regulations, intervening in cases of non-compliance and imposing penalties for violations related to energy rates, market practices, and licensing.
- NERC: Focuses on reliability compliance, conducting audits, and issuing penalties if utilities or power companies do not adhere to reliability standards.
How NERC and FERC Collaborate
The roles of NERC and FERC often intersect, as both organizations are integral to maintaining the power system’s overall stability and safety. Here’s how they collaborate to achieve shared objectives:
Standard Development and Approval
NERC develops reliability standards, which FERC then reviews and approves. This process ensures that standards are robust, current, and adaptable to evolving technological and environmental needs.
Compliance Oversight
While NERC monitors utilities for compliance with reliability standards, FERC provides an additional layer of enforcement, particularly when non-compliance impacts the broader market. FERC’s backing enhances NERC’s ability to hold entities accountable for reliability issues.
Event Analysis and System Resilience
After significant disturbances or failures, NERC conducts in-depth analyses, which are crucial for updating standards and improving resilience. FERC then incorporates these insights into broader policy updates, ensuring that reliability measures align with market needs.
The Role of NERC Operation and Planning Standards in Today’s Grid
NERC’s Operation and Planning Standards play a foundational role in the reliability of the North American electric grid. By focusing on operational readiness and future system planning, these standards help mitigate risks associated with power outages, equipment failures, and extreme weather conditions. NERC’s standards cover:
- Operational Standards: Focus on real-time responses, ensuring grid operators can manage unexpected changes or emergencies through effective system monitoring, control, and communication.
- Planning Standards: Address long-term planning needs, allowing utilities to assess resource adequacy, future demand, and potential reliability challenges.
The standards are also continuously updated to accommodate new technology trends, including renewable energy integration, cybersecurity, and distributed energy resources, ensuring that the power grid remains resilient in a dynamic environment.
Why Understanding the Difference Matters for Utility Companies
For utility companies, distinguishing between FERC and NERC’s responsibilities is essential to maintaining compliance and operational excellence. FERC’s oversight can directly impact financial aspects, such as pricing and licensing, while NERC’s standards ensure grid reliability. Understanding each organization’s focus allows utilities to:
- Strategically Allocate Resources: Utility companies can better allocate resources to meet FERC’s regulatory standards while simultaneously maintaining compliance with NERC’s reliability guidelines.
- Stay Proactive in Compliance: By being aware of FERC’s enforcement approach and NERC’s operational standards, utilities can avoid penalties and improve system resilience.
- Adapt to Industry Changes: NERC and FERC’s roles in supporting the energy transition to renewables and smart grids allow utilities to stay ahead of regulatory shifts and technological advances.
The Future of NERC and FERC in the Evolving Energy Landscape
As the energy industry evolves toward renewable energy sources and smart grid technologies, the responsibilities of NERC and FERC will continue to adapt. For instance, NERC is now focusing on incorporating distributed energy resources and enhancing cybersecurity measures to keep the grid secure. Meanwhile, FERC will likely play an essential role in supporting this transition by establishing market conditions conducive to renewable energy.
Together, FERC and NERC’s complementary roles in regulation and reliability will be critical to supporting a sustainable and resilient energy infrastructure in North America.
Trust Keentel Engineering for Your Power System Needs
At Keentel Engineering, we understand the intricacies of FERC and NERC regulations and their implications for power system planning and reliability. With over two decades of experience, our team is well equipped to help you navigate compliance challenges, implement robust reliability standards, and ensure your power systems meet both regulatory and operational requirements. Whether you’re looking for system design, control, or analysis, we provide innovative solutions that will elevate your business. Contact us today to learn how we can support your power system and engineering needs and drive your business forward.

About the Author:
Sonny Patel P.E. EC
IEEE Senior Member
In 1995, Sandip (Sonny) R. Patel earned his Electrical Engineering degree from the University of Illinois, specializing in Electrical Engineering . But degrees don’t build legacies—action does. For three decades, he’s been shaping the future of engineering, not just as a licensed Professional Engineer across multiple states (Florida, California, New York, West Virginia, and Minnesota), but as a doer. A builder. A leader. Not just an engineer. A Licensed Electrical Contractor in Florida with an Unlimited EC license. Not just an executive. The founder and CEO of KEENTEL LLC—where expertise meets execution. Three decades. Multiple states. Endless impact.
Services

Let's Discuss Your Project
Let's book a call to discuss your electrical engineering project that we can help you with.

About the Author:
Sonny Patel P.E. EC
IEEE Senior Member
In 1995, Sandip (Sonny) R. Patel earned his Electrical Engineering degree from the University of Illinois, specializing in Electrical Engineering . But degrees don’t build legacies—action does. For three decades, he’s been shaping the future of engineering, not just as a licensed Professional Engineer across multiple states (Florida, California, New York, West Virginia, and Minnesota), but as a doer. A builder. A leader. Not just an engineer. A Licensed Electrical Contractor in Florida with an Unlimited EC license. Not just an executive. The founder and CEO of KEENTEL LLC—where expertise meets execution. Three decades. Multiple states. Endless impact.
Leave a Comment
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.