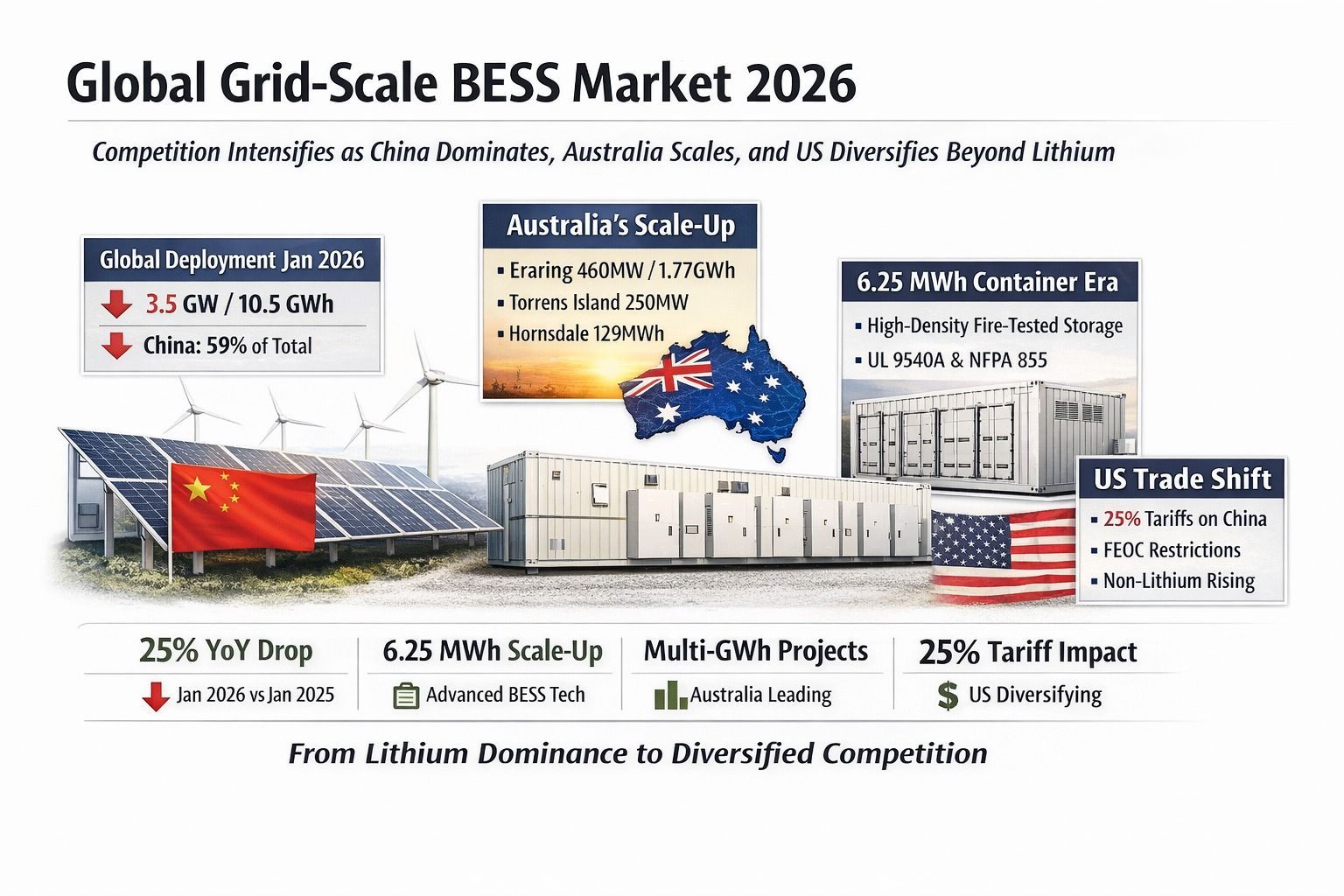
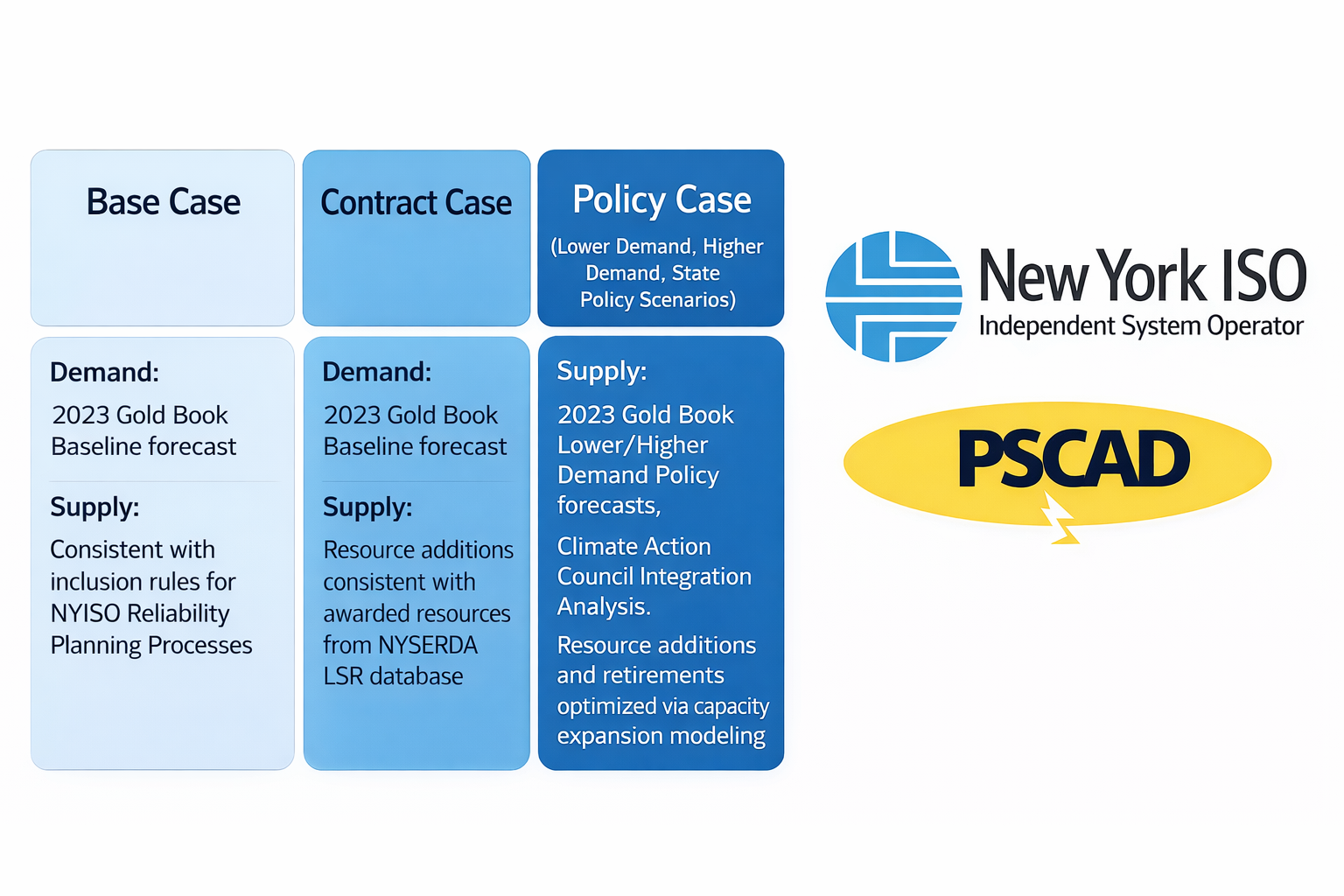
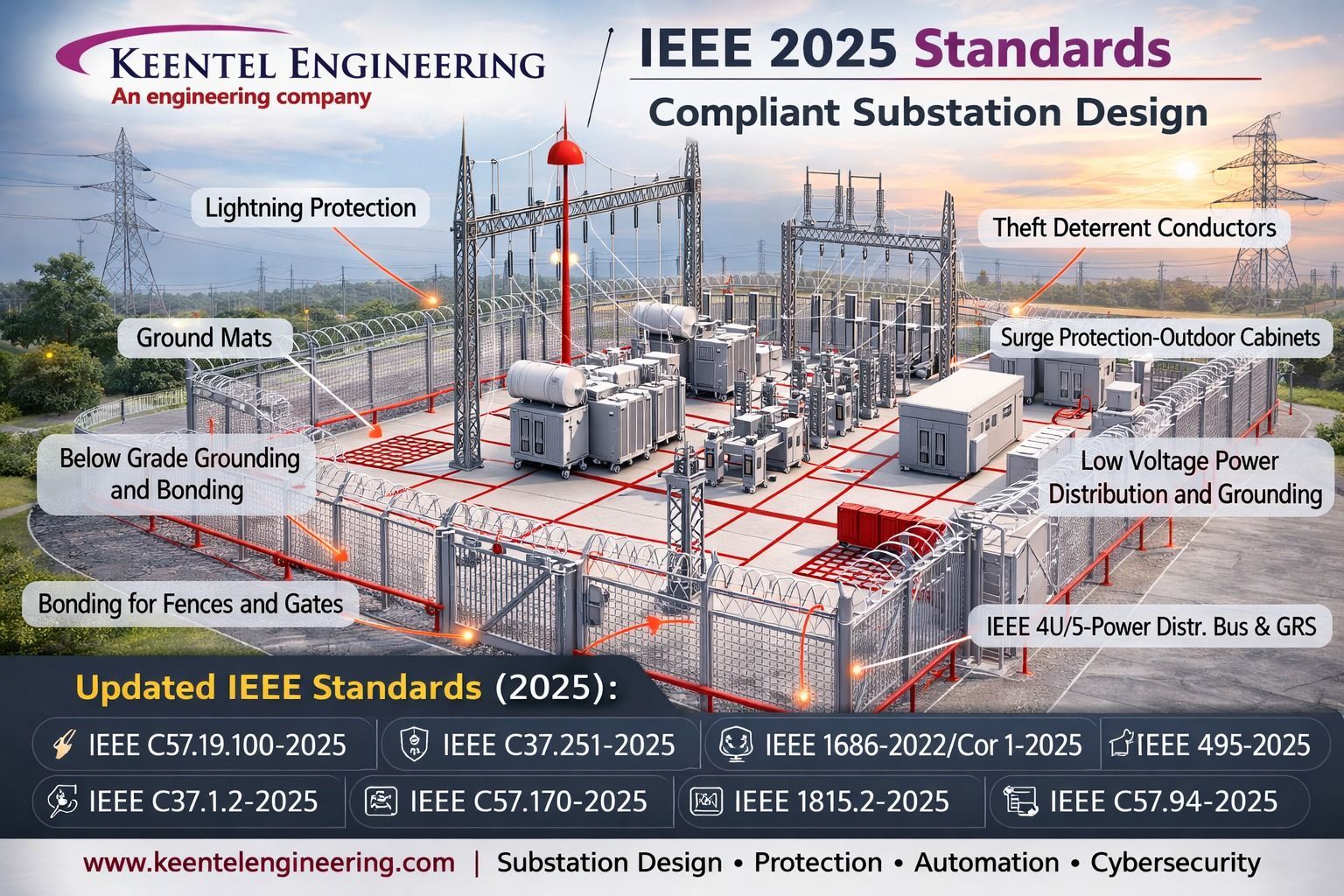
A Coordinated Electric System Interconnection Review—the utility’s deep-dive on technical and cost impacts of your project.
SPP 2025 ITP Assessment: Enhancing Transmission Planning for a Resilient Energy Future
May 9, 2025 | Blog

Keentel Engineering continues its commitment to energy reliability and innovation by aligning with the latest industry developments. The 2025 Integrated Transmission Planning (ITP) Assessment, issued by the Southwest Power Pool (SPP), is a foundational blueprint for regional energy delivery. This detailed assessment emphasizes resiliency, public policy integration, and economic optimization—key priorities for utilities, regulators, and infrastructure partners.
What is the 2025 ITP?
The ITP is a regional planning initiative designed to deliver:
- Reliable transmission systems.
- Economical energy distribution.
- Policy-aligned infrastructure investments.
For 2025, the scope is broader and deeper, integrating lessons from extreme weather events and surging energy demands driven by electric vehicles (EVs) and data centers. Learn how we support these trends with our Battery Energy Storage Systems engineering services.
Key Elements of the 2025 ITP
Dual Futures Framework
- Future 1: Reference Case – Based on current trends.
- Future 2: Emerging Technologies – Incorporates rapid EV growth, renewables, and data center load spikes.
Resiliency-Centric Planning
- Summer Stress Conditions – Drought, high temps, and generation maintenance issues.
- Winter Outages – Fuel shortages, ice storms, and forced outages.
- High Load Growth – Driven by emerging technologies and unexpected demand.
Updated Generator & Resource Models
- EIA’s 2023 cost and performance data for generator prototypes.
- Planning reserve margins: 16% for summer, up to 35% for winter.
- Tiered resource accreditation for better grid forecasting.
- Increased solar, wind, and storage capacities, especially in Future 2.
Public Policy and Renewable Standards
- State RPS goals drive allocations (e.g., New Mexico: 40% by Year 5; Colorado: 30%).
- SPP assigns 100% of non-policy requests and aligns 50% of policy additions to wind and 50% to solar.
Technical Depth: Key Metrics and Tools
Load and Generation Projections
- Peak loads for resiliency scenarios: over 70 GW in Year 10.
- Wind and solar capacity modeled with conservative capacity factors.
Economic Models
- Market Economic Models (MEMs) assess costs, prices, and congestion.
- RMEMs overlay resiliency events to evaluate Locational Marginal Pricing (LMP) spikes.
Portfolio Development
Projects are scored on:
- Congestion relief.
- Operational impact.
- Long-term benefits and resiliency mitigation.
Why This Matters for Keentel Clients
Keentel Engineering leverages insights from the 2025 ITP to:
- Guide infrastructure designs resilient to climate extremes.
- Support utilities in meeting state RPS goals.
- Ensure alignment with SPP’s economic and reliability priorities.
Whether you’re investing in renewable integration, enhancing transmission lines, or modeling load growth for new commercial corridors—our strategies are informed by SPP’s most advanced planning initiative yet.
FAQs on the 2025 ITP Assessment Scope
1. What is the primary goal of the 2025 ITP?
To develop a regional transmission plan that ensures reliability, affordability, and public policy compliance.
2. Who oversees the 2025 ITP?
SPP’s Economic Studies Working Group (ESWG), Transmission Working Group (TWG), and the Market Operations and Policy Committee (MOPC).
3. What are the planning years used?
2025 (Year 1), 2026 (Year 2), 2029 (Year 5), and 2034 (Year 10).
4. What are Futures 1 and 2?
Scenarios that reflect moderate (F1) and high-growth/emerging tech (F2) demand conditions.
5. What are the key resiliency scenarios?
Summer stress, winter outages, and EV-driven load spikes.
6. What is the Planning Reserve Margin (PRM)?
16% for summer, 27% (2029), and 35% (2034) for winter.
7. How are resources accredited?
Using Effective Load Carrying Capability (ELCC) with Tier 1 and Tier 2 resource classifications.
8. How does SPP define “must-run” units?
Hydro, nuclear, landfill gas, and co-gen units unless exceptions apply.
9. What role do curtailment prices play?
They reflect tax credits and impact dispatch in economic models.
10. What are hurdle rates?
They simulate interregional transaction costs and are adjusted based on vendor data.
11. How is resiliency need assessed?
Using LMP impact, transferability between zones, and potential for load shedding.
12. What is the Southeastern SPP target area?
A region flagged by AEP for low voltages, high congestion, and stability issues.
13. How is generation assigned in modeling?
Based on policy, utility requests, and resource planning templates.
14. What are generator prototypes?
Standardized generation models using EIA data for economic simulations.
15. How is storage modeled?
Storage capacities increase in later years; e.g., 19.2 GW in Year 10 for Future 2.
16. What is the role of Distributed Generation?
Included based on utility submissions but excluded from detailed control modeling.
17. How are extreme events simulated?
Through monthly model alterations (e.g., January and July) to reflect stress.
18. How is LMP used for planning?
To identify constrained, high-value generators during peak demand.
19. How does SPP handle load additions?
Through forecast validation and inclusion in Future 2 spot load scenarios.
20. What are MEM and RMEM?
Market Economic Models with and without resiliency overlays.
21. How is project value measured?
By a scoring matrix including APC benefits, congestion relief, and viability.
22. What is the ITP project timeline?
Runs from July 2023 to October 2025.
23. How are voltage stability and sensitivities handled?
Through final assessments using consolidated portfolios and TWG input.
24. How does SPP address evolving assumptions?
By formally revising the scope under stakeholder protocols.
25. How can stakeholders participate?
Through working group engagements, model reviews, and the solution vetting process.
Learn more about our Power System Studies
Explore our POI Interconnection Engineering Support
Ready to future-proof your transmission planning? Contact Keentel Engineering today.

About the Author:
Sonny Patel P.E. EC
IEEE Senior Member
In 1995, Sandip (Sonny) R. Patel earned his Electrical Engineering degree from the University of Illinois, specializing in Electrical Engineering . But degrees don’t build legacies—action does. For three decades, he’s been shaping the future of engineering, not just as a licensed Professional Engineer across multiple states (Florida, California, New York, West Virginia, and Minnesota), but as a doer. A builder. A leader. Not just an engineer. A Licensed Electrical Contractor in Florida with an Unlimited EC license. Not just an executive. The founder and CEO of KEENTEL LLC—where expertise meets execution. Three decades. Multiple states. Endless impact.
Services

Let's Discuss Your Project
Let's book a call to discuss your electrical engineering project that we can help you with.

About the Author:
Sonny Patel P.E. EC
IEEE Senior Member
In 1995, Sandip (Sonny) R. Patel earned his Electrical Engineering degree from the University of Illinois, specializing in Electrical Engineering . But degrees don’t build legacies—action does. For three decades, he’s been shaping the future of engineering, not just as a licensed Professional Engineer across multiple states (Florida, California, New York, West Virginia, and Minnesota), but as a doer. A builder. A leader. Not just an engineer. A Licensed Electrical Contractor in Florida with an Unlimited EC license. Not just an executive. The founder and CEO of KEENTEL LLC—where expertise meets execution. Three decades. Multiple states. Endless impact.
Leave a Comment
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.
Related Posts