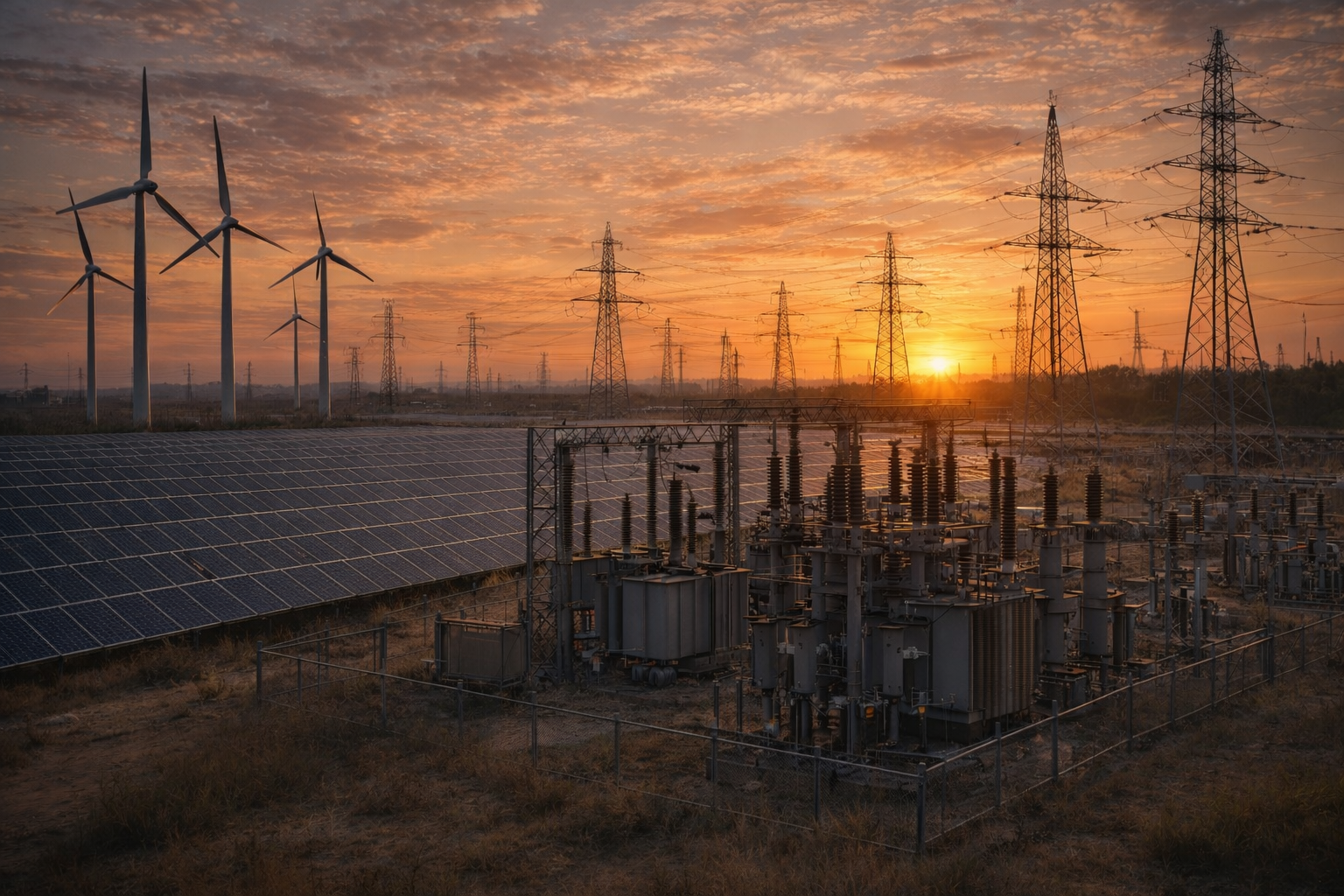
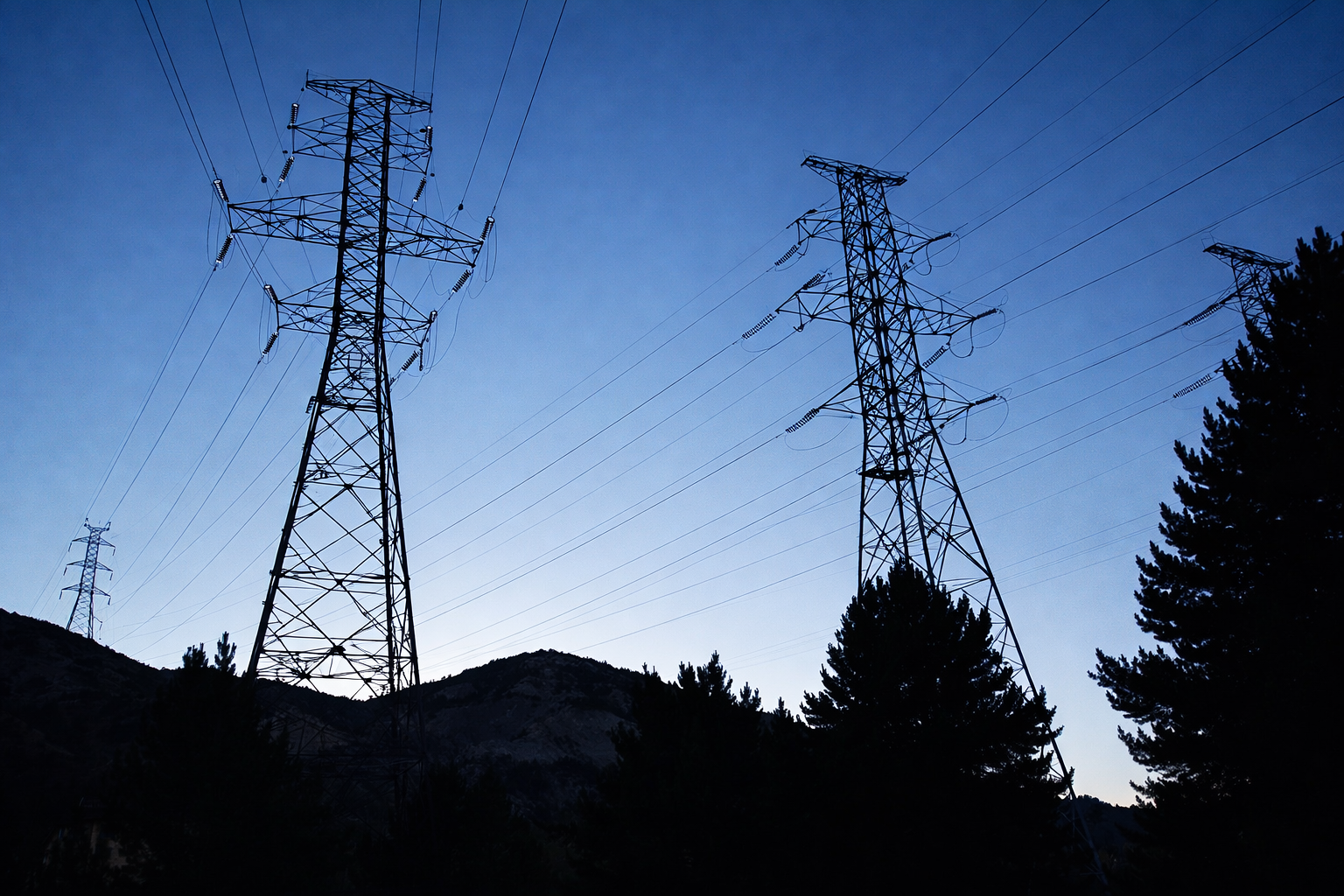
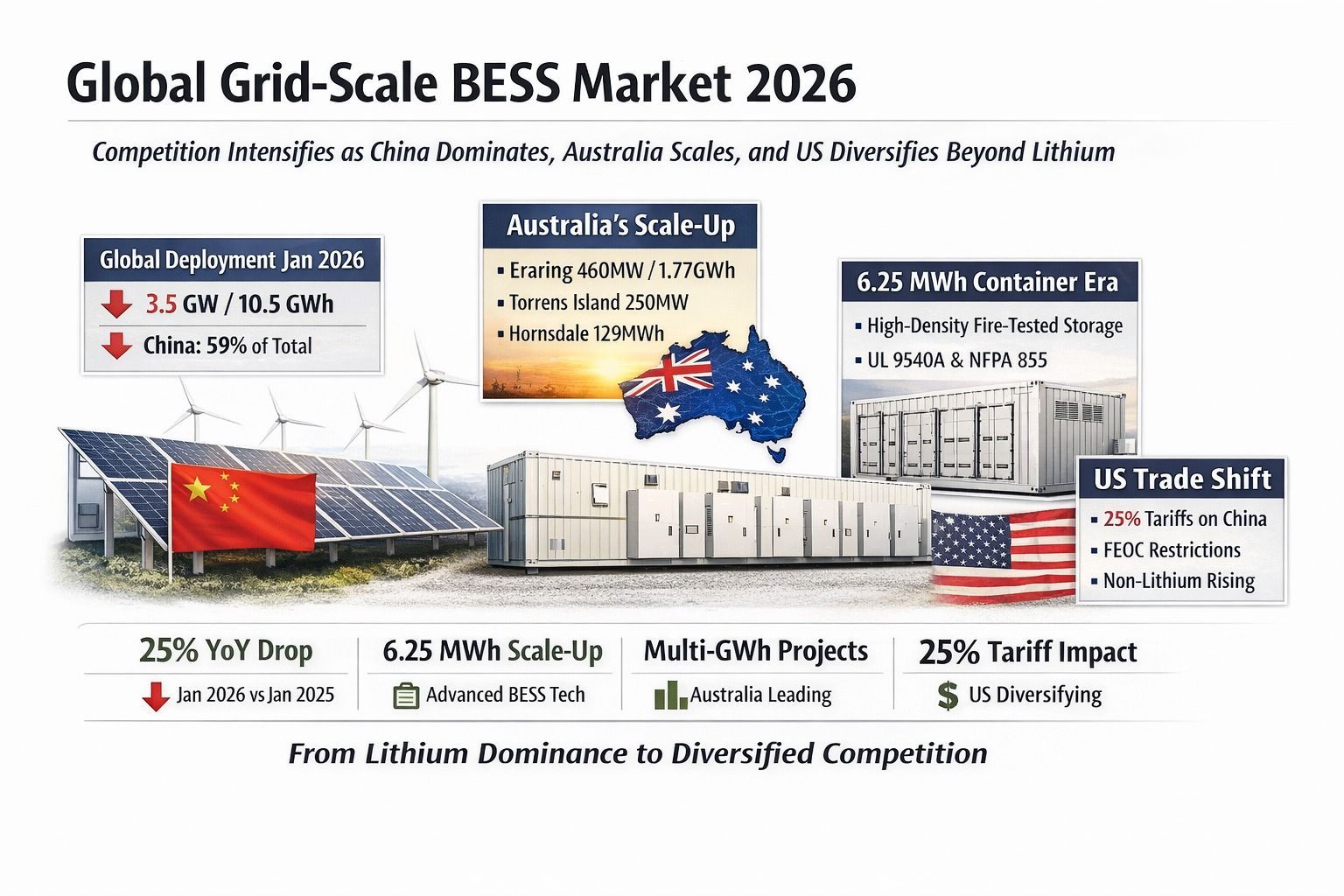
A Coordinated Electric System Interconnection Review—the utility’s deep-dive on technical and cost impacts of your project.
Key Benefits of Electrical Substation Design for Modern Power Systems
January 17, 2022 | Blog

Electrical substations play a critical role in today’s power infrastructure by enabling safe, reliable, and efficient electricity delivery. Modern electrical substation design ensures proper voltage transformation, system protection, and real-time monitoring across transmission and distribution networks. As utilities expand capacity and integrate renewable energy, well-engineered substations have become essential to maintaining grid stability and long-term reliability.
A properly designed substation improves substation reliability, enhances operational safety, and supports future grid expansion. From high-voltage transmission yards to power distribution substations, electrical substations form the backbone of modern power systems.
What Is an Electrical Substation and What Does It Do?
An electrical substation is a facility that transforms voltage levels, controls power flow, and protects the electrical grid. Substations step down high-voltage electricity from transmission systems to lower voltages suitable for distribution to homes, businesses, and industrial facilities.
The main purpose of a power substation includes:
- Voltage transformation
- Circuit switching and isolation
- System protection and fault detection
- Grid monitoring and control
Without substations, electricity could not be delivered safely or efficiently across the power network.
Why Electrical Substation Design Is Critical to Power Distribution
Substation design is a cornerstone of power system engineering. Poor design can lead to equipment failure, unsafe operating conditions, and widespread outages. A well-planned electric substation design ensures efficient power delivery while protecting people, assets, and infrastructure.
Modern substations support:
- Reliable power distribution
- Load balancing and system control
- Fault isolation and grid resilience
- Compliance with NESC and IEEE standards
As power demand increases and grids evolve, utility-scale substation design becomes increasingly important for long-term performance.
Key Components of Electrical Substation Engineering
Electrical substation engineering integrates multiple systems into a structured and safe operating environment. A typical substation layout showing substation equipment includes:
High-Voltage Switchyard and Power Entry
Incoming transmission lines connect to a high voltage switchyard (HV switchyard) containing circuit breakers, disconnect switches, and surge protection devices. This area enables safe switching, fault interruption, and maintenance isolation.
Power Transformers
Transformers convert voltage levels between transmission and distribution systems. Reliable substation transformers are critical for voltage regulation and load control.
Substation Protection and Control Design
Protective relays, breakers, and control systems detect faults and isolate affected sections of the grid. Proper substation protection design minimizes outages and equipment damage.
SCADA and Smart Substation Technology
Modern substations use SCADA systems and intelligent electronic devices to enable real-time monitoring, automation, and remote operation—key features of a smart substation
Substation Layout, Expansion, and Future-Ready Design
Substation Layout, Expansion, and Future-Ready Design
A well-planned substation layout directly impacts safety, reliability, and expandability. Layout decisions influence grounding performance, arc-flash mitigation, and maintenance accessibility.
What Makes a Substation Design Resilient and Future-Ready?
A future-ready design includes:
- Modular bus configurations
- Space for additional feeders and transformers
- IEC 61850-compliant protection and communication
- SCADA-ready control panels
Which High Voltage Substation Setups Are Easiest to Expand?
Ring-bus and breaker-and-a-half configurations are among the easiest high-voltage substation setups to expand, allowing utilities to add capacity with minimal outages.
Types of Electrical Substation Designs for Modern Power Systems
High-Voltage and Bulk Power Substations
High-voltage substations manage bulk power transfer across the grid. Common designs include 115 kV, 230 kV, and 500 kV substations, including 500 kV bulk power substation design for large transmission interconnections.
Utility-Scale and Power Distribution Substations
Utility substation design focuses on reliability, safety, and regulatory compliance. These substations support power distribution substation design and ensure consistent electricity delivery to end users.
Renewable Energy and BESS Substations
Renewable energy substation design supports solar, wind, and battery energy storage systems (BESS). These substations manage variable generation, grid interconnection, and energy dispatch while maintaining stability.
Key Benefits of Electrical Substation Design
1. Improved Substation Reliability
Advanced protective relays and high-speed breakers isolate faults quickly, preventing widespread outages and maintaining service continuity.
2. Enhanced Safety and Code Compliance
Substations designed to meet NESC and IEEE 80 standards reduce arc-flash risk, improve grounding performance, and protect personnel.
3. Reduced Energy Losses
Optimized layouts and transformer loading reduce losses across transmission and distribution networks, improving overall efficiency.
4. Scalable Infrastructure for Grid Growth
Modern substations are engineered for future expansion, supporting EV charging, renewable integration, and load growth without costly redesigns.
5. Real-Time Monitoring and Control
SCADA-enabled substations provide real-time diagnostics, remote switching, and predictive maintenance capabilities—key advantages of substation monitoring.
Which High Voltage Substation Configurations Offer the Best Reliability?
Breaker-and-a-half and double-bus configurations offer the highest reliability for high-voltage substations in the United States. These designs provide superior fault isolation, operational flexibility, and maintenance capability without service interruption.
Why Electrical Substation Engineering Matters for Grid Modernization
As utilities modernize infrastructure, electrical substation engineering plays a vital role in grid electrification and resilience. Proper engineering ensures substations can support renewable energy, digital protection systems, and evolving load requirements.
Keentel Engineering integrates grounding systems, IEC 61850-compliant relays, and SCADA-ready controls into every design, supporting safe and efficient grid modernization.
Why Choose Keentel Engineering for Substation Design?
- Licensed Professional Engineers (P.E.) across multiple U.S. states
- Expertise in HV, utility, and industrial substation design
- Proven experience with SCADA and IEC 61850 systems
- End-to-end services from concept to commissioning
- Integrated power system studies for compliance and performance
Whether planning a new transmission yard or upgrading a power distribution substation, Keentel Engineering delivers compliant, cost-effective, and future-ready solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is an electrical substation?
An electrical substation is a facility that transforms voltage levels, controls power flow, and protects the electrical grid by isolating faults and enabling safe system operation.
2. What does a substation do in a power system?
A substation steps up or down the voltage, switches electrical circuits, protects equipment from faults, and ensures reliable electricity delivery across transmission and distribution networks.
3. What is the main purpose of a power substation?
The main purpose of a power substation is to convert high-voltage electricity into safe, usable levels while regulating voltage and maintaining grid stability.
4. Why is electrical substation design important?
Electrical substation design is important because it ensures system reliability, operational safety, voltage control, and compliance with engineering standards such as NESC and IEEE.
5. What are the key components of an electrical substation?
Key components include power transformers, circuit breakers, disconnect switches, busbars, grounding systems, protective relays, and SCADA-based control systems.
6. Which high-voltage substation configurations offer the best reliability?
Breaker-and-a-half and double-bus configurations offer the best reliability by allowing fault isolation and maintenance without interrupting power delivery.
7. What makes a substation design resilient and future-ready?
A resilient and future-ready substation design includes modular layouts, IEC 61850-compliant protection systems, SCADA integration, and space for future expansion.
8. What is a substation layout?
A substation layout defines the physical arrangement of equipment such as transformers, switchyards, and control buildings to ensure safety, reliability, and efficient maintenance
9. How do substations support renewable energy integration?
Substations support renewable energy integration by managing voltage regulation, grid interconnection, protection, and power quality for solar, wind, and battery energy storage systems.
10. How does SCADA improve substation operations?
SCADA systems improve substation operations by providing real-time monitoring, remote switching, fault detection, and faster response to system disturbances.
Next Step
Planning a new yard or upgrading legacy gear? Email contact@keentelengineering.com or call +1 (813) 389-7871 for a free design scoping session.

About the Author:
Sonny Patel P.E. EC
IEEE Senior Member
In 1995, Sandip (Sonny) R. Patel earned his Electrical Engineering degree from the University of Illinois, specializing in Electrical Engineering . But degrees don’t build legacies—action does. For three decades, he’s been shaping the future of engineering, not just as a licensed Professional Engineer across multiple states (Florida, California, New York, West Virginia, and Minnesota), but as a doer. A builder. A leader. Not just an engineer. A Licensed Electrical Contractor in Florida with an Unlimited EC license. Not just an executive. The founder and CEO of KEENTEL LLC—where expertise meets execution. Three decades. Multiple states. Endless impact.
Services

Let's Discuss Your Project
Let's book a call to discuss your electrical engineering project that we can help you with.

About the Author:
Sonny Patel P.E. EC
IEEE Senior Member
In 1995, Sandip (Sonny) R. Patel earned his Electrical Engineering degree from the University of Illinois, specializing in Electrical Engineering . But degrees don’t build legacies—action does. For three decades, he’s been shaping the future of engineering, not just as a licensed Professional Engineer across multiple states (Florida, California, New York, West Virginia, and Minnesota), but as a doer. A builder. A leader. Not just an engineer. A Licensed Electrical Contractor in Florida with an Unlimited EC license. Not just an executive. The founder and CEO of KEENTEL LLC—where expertise meets execution. Three decades. Multiple states. Endless impact.
Leave a Comment
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.
Related Posts