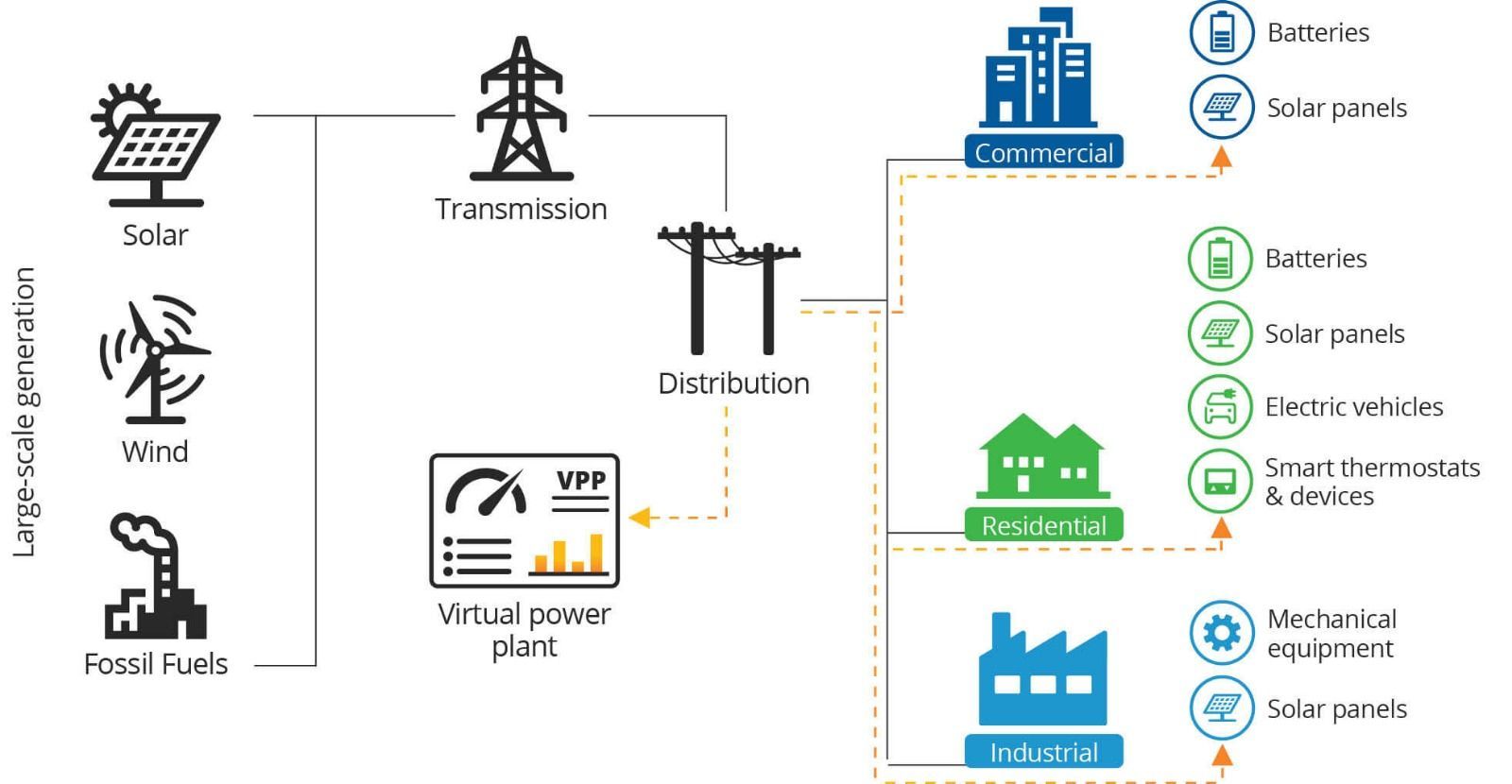
A Coordinated Electric System Interconnection Review—the utility’s deep-dive on technical and cost impacts of your project.
Challenge: Frequent false tripping using conventional electromechanical relays
Solution: SEL-487E integration with multi-terminal differential protection and dynamic inrush restraint
Result: 90% reduction in false trips, saving over $250,000 in downtime
| Category | Metric |
|---|---|
| VPP capacity (Lunar Energy) | 650 MW |
| Lunar funding raised | US$232 million |
| Data center BESS example | 31 MW / 62 MWh |
| ERCOT grid-scale batteries | 15+ GW |
| LDES tenders (H1 2026) | Up to 9.3 GW |
| Lithium-ion share of LDES by 2030 | 77% |
| FEOC initial threshold | 55% |
| BESS tariff rate (2026) | ~55% |
| Capacity gain from analytics | 5–15% |
BIM Beyond Traditional Substation Design: Transforming the Utility Project Lifecycle
February 19, 2026 | Blog
Introduction
For decades, substation design relied heavily on 2D drawings, discipline-specific workflows and isolated datasets. While model-based design introduced 3D modeling, automated drawings, and clash detection, the focus remained largely on physical layout and construction documentation.
Today, utilities are transitioning from model-based design to a data-driven BIM (Building Information Modeling) framework a shift that transforms the 3D model from a drawing tool into a centralized data ecosystem supporting the entire project lifecycle.
BIM is not software. It is a workflow philosophy that prioritizes data interoperability, lifecycle integration, and a “single source of truth” approach across planning, engineering, procurement, construction, operations, and maintenance.
This article explores how BIM extends far beyond traditional substation design and unlocks strategic value across utility infrastructure.
What Is BIM in Utility Substation Projects?
BIM (Building Information Modeling) is a lifecycle-oriented workflow that integrates:
- Conceptual design
- Cost estimating
- Detailed engineering
- Procurement
- Construction planning
- Asset management
- Operations and maintenance
Unlike traditional workflows where each stakeholder creates separate datasets, BIM centralizes project information into a shared, interoperable data model.
In a utility project, multiple groups require different information:
| Stakeholder | Required Information |
|---|---|
| Public Relations | Visual impact, site footprint |
| Engineering | Electrical & structural parameters |
| Procurement | Cost, vendor data, delivery schedule |
| Construction | Installation sequencing, equipment needs |
| O&M | Maintenance procedures, asset data |
Without BIM, these datasets are recreated repeatedly. With BIM, they derive from the same intelligent model.
The Limitation of Traditional Model-Based Substation Design
Traditional 3D modeling provides:
- Automated drawings
- Bill of Materials (BOM)
- Clearance checks
- Clash detection
However, in many workflows, engineering analysis data is generated in external applications and manually transferred to the model. This creates:
- Data silos
- Duplicate effort
- Increased error risk
- Reduced lifecycle usability
BIM addresses this through data interoperability, enabling seamless data exchange between analysis software, design tools, GIS platforms, and asset management systems.
BIM Applications Across the Substation Lifecycle
1. Conceptual Design & Project Visualization
During early project phases, speed and adaptability are critical.
A BIM-driven 3D model allows teams to:
- Quickly assemble layouts from standard component libraries
- Visualize site development and landscaping
- Present projects at permitting and public meetings
- Evaluate design alternatives instantly
Design changes can immediately reflect cost impacts when data is embedded in the model. This transforms stakeholder engagement from static drawings to interactive visualization.
2. Detailed Engineering with Data Integration
In the engineering phase, the conceptual model evolves into a data-rich digital asset.
Key improvements include:
- Embedded equipment parameters
- Structural load data
- Electrical analysis integration
- Automated BOM synchronization
- Reduced manual data transfer
The core feature of BIM is interoperability not software selection.
Engineering tools must exchange data freely to:
- Reduce rework
- Eliminate duplication
- Maintain consistency across disciplines
3. VR & AR Integration
One of the most powerful BIM extensions is immersive technology integration.
Virtual Reality (VR)
- Cross-disciplinary design reviews
- Spatial validation
- Clearance verification
- Improved stakeholder communication
Augmented Reality (AR)
- Overlay digital models onto physical environments
- Construction assistance
- Installation validation
- Maintenance training
These technologies enhance collaboration and improve execution quality.
4. GIS Integration for Risk Reduction
Resource Entities must provide updated dynamics data when:
- Equipment is replaced
- Settings are changed
- Field tests indicate model inaccuracies
5. Procurement & Construction Intelligence
A BIM model can embed procurement data at the component level, including:
- Purchase order references
- Vendor details
- Lead times
- Delivery schedules
For construction:
- Installation equipment requirements
- Sequencing linked to schedule
- Labor projections
- Progress tracking (planned vs. actual)
- Submittal and RFI management
This transforms the model into a construction and project management platform — not just a design file.
Future Possibilities of BIM in Utility Infrastructure
1. Asset Health Monitoring & Predictive Maintenance
By integrating sensors with BIM:
- Real-time equipment monitoring becomes possible
- Historical data supports predictive analytics
- Lifespan modeling improves replacement planning
- Failure risks decrease
This supports digital twin strategies for substations.
2. Remote Maintenance via AR
With enriched data models and AR integration:
- Field technicians receive remote guidance
- Maintenance procedures overlay equipment in real time
- Training becomes immersive and accurate
3. Sustainability & Embodied Carbon Tracking
One of BIM’s strongest capabilities is handling large datasets.
Utilities can track sustainability metrics such as:
- Embodied carbon
- Material quantities
- Emissions impact
- Design alternatives aligned with greenhouse gas reduction goals
Instead of manually tracking material emissions across multiple substations, BIM centralizes sustainability data at the component level. This enables utilities to choose design options that meet carbon reduction targets.
4. Generative Design for Substations
Generative design combines human-defined constraints with computational power.
Computers can generate multiple design options based on:
- Clearance requirements
- Fence layout constraints
- Environmental limitations
- Land cost minimization
- Schedule optimization
The design team then selects the most optimized option.
For substations, this can result in:
- Reduced footprint
- Lower material usage
- Improved constructability
- Minimized environmental impact
BIM as a Strategic Infrastructure Platform
While traditional model-based design improves construction drawings, BIM expands value across the full lifecycle.
Key benefits include:
- Single source of truth
- Reduced human error
- Improved stakeholder coordination
- Enhanced lifecycle visibility
- Long-term operational intelligence
- Greater sustainability alignment
BIM transforms substations from static facilities into data-driven infrastructure assets.
Form 2115 FAQ – 20 Technical Questions & Answers
1. What is BIM in substation design?
BIM is a lifecycle-based workflow that centralizes project data into a single interoperable model supporting planning through maintenance.
2. Is BIM software?
No. BIM is a methodology. Multiple software tools can support BIM as long as data interoperability exists.
3. How does BIM differ from 3D modeling?
3D modeling focuses on geometry. BIM focuses on structured data and lifecycle integration.
4. Why is data interoperability critical?
It prevents duplicate effort, manual transfers, and inconsistent datasets across disciplines.
5. How does BIM improve public engagement?
It enables visual presentations and instant cost impact updates during conceptual design.
6. Can BIM integrate with GIS?
Yes. GIS layers such as flood zones and environmental maps can overlay design models for risk analysis.
7. How does BIM support procurement?
Components can contain embedded vendor, lead time, and purchasing data.
8. How does BIM help construction sequencing?
The model can link to schedules, enabling visual construction planning and labor forecasting.
9. Can BIM track RFIs and submittals?
Yes. BIM platforms can integrate construction documentation tracking.
10. What role does VR play in BIM?
VR enables immersive design review and stakeholder collaboration.
11. How does AR assist in substations?
AR overlays digital information onto physical equipment for installation and maintenance support.
12. What is a digital twin?
A digital twin is a live data-enabled BIM model integrated with real-time sensor data.
13. How does BIM support predictive maintenance?
Sensor data embedded in BIM enables lifespan prediction and proactive replacement planning.
14. Can BIM track embodied carbon?
Yes. Sustainability metrics can be assigned at the component level.
15. How does BIM support greenhouse gas reduction goals?
It enables comparison of design alternatives based on emissions data.
16. What is generative design?
A computational method that produces multiple optimized design solutions based on constraints.
17. How can generative design apply to substations?
By optimizing layout, footprint, fence positioning, and clearance compliance.
18. Does BIM eliminate human error?
It significantly reduces manual data entry errors but still requires engineering oversight.
19. What lifecycle stages benefit most from BIM?
Operations and maintenance benefit most due to long asset lifespans.
20. Why is BIM considered the future of utility design?
Because it extends beyond drawings into data intelligence, asset management, and sustainability

About the Author:
Sonny Patel P.E. EC
IEEE Senior Member
In 1995, Sandip (Sonny) R. Patel earned his Electrical Engineering degree from the University of Illinois, specializing in Electrical Engineering . But degrees don’t build legacies—action does. For three decades, he’s been shaping the future of engineering, not just as a licensed Professional Engineer across multiple states (Florida, California, New York, West Virginia, and Minnesota), but as a doer. A builder. A leader. Not just an engineer. A Licensed Electrical Contractor in Florida with an Unlimited EC license. Not just an executive. The founder and CEO of KEENTEL LLC—where expertise meets execution. Three decades. Multiple states. Endless impact.
Services

Let's Discuss Your Project
Let's book a call to discuss your electrical engineering project that we can help you with.

About the Author:
Sonny Patel P.E. EC
IEEE Senior Member
In 1995, Sandip (Sonny) R. Patel earned his Electrical Engineering degree from the University of Illinois, specializing in Electrical Engineering . But degrees don’t build legacies—action does. For three decades, he’s been shaping the future of engineering, not just as a licensed Professional Engineer across multiple states (Florida, California, New York, West Virginia, and Minnesota), but as a doer. A builder. A leader. Not just an engineer. A Licensed Electrical Contractor in Florida with an Unlimited EC license. Not just an executive. The founder and CEO of KEENTEL LLC—where expertise meets execution. Three decades. Multiple states. Endless impact.
Leave a Comment
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.