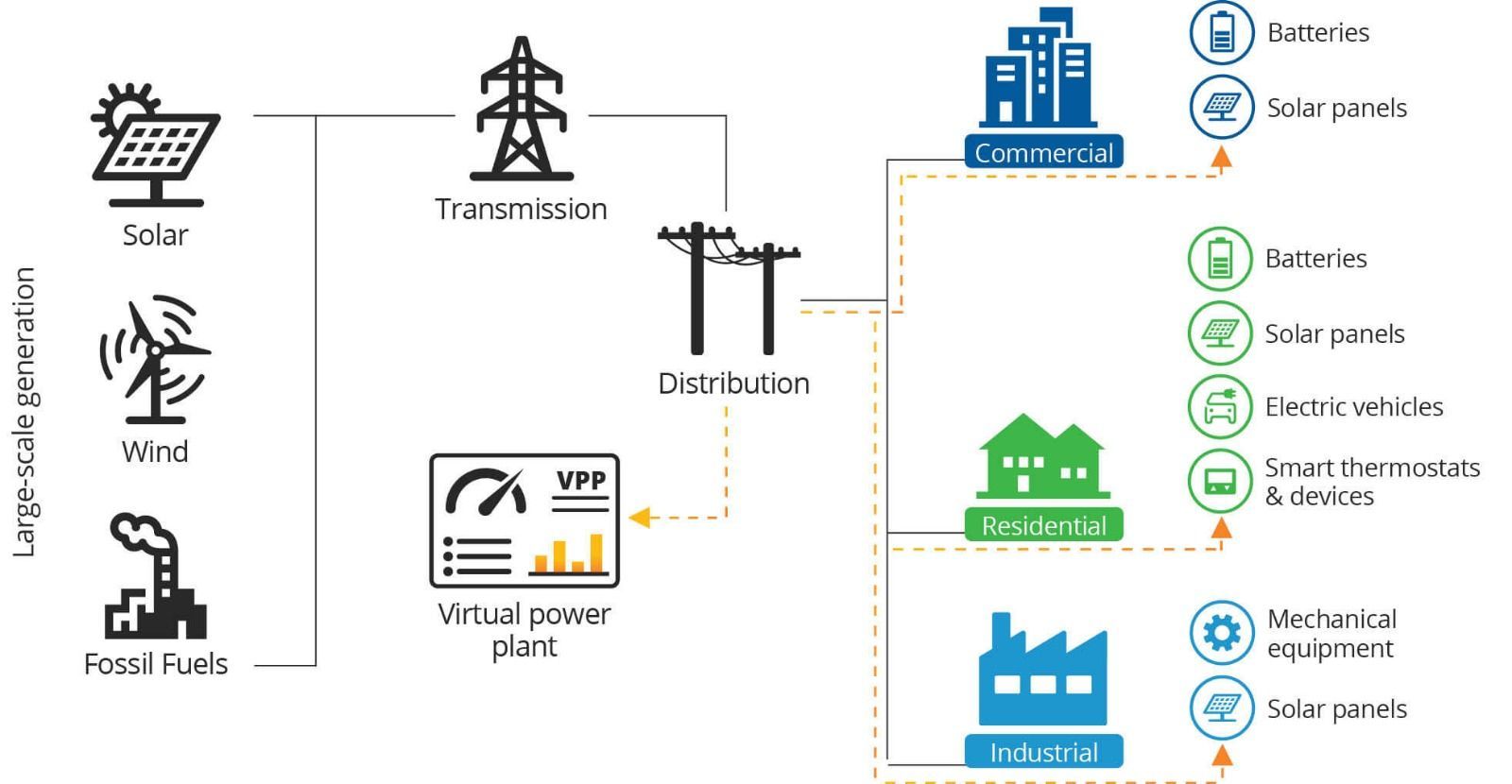
A Coordinated Electric System Interconnection Review—the utility’s deep-dive on technical and cost impacts of your project.
Challenge: Frequent false tripping using conventional electromechanical relays
Solution: SEL-487E integration with multi-terminal differential protection and dynamic inrush restraint
Result: 90% reduction in false trips, saving over $250,000 in downtime
Navigating NERC PRC-029-1: A Practical Guide for Inverter-Based Resource Owners
December 17, 2025 | Blog
On july24, 2025, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) issued Order 909, approving NERC PRC-029-1, a new reliability standard establishing mandatory frequency and voltage ride-through performance requirements for inverter-based resources (IBRs). Alongside the adoption of PRC-024-4 for synchronous generators, this marks a significant shift in how grid-connected resources are expected to support the Bulk Power System (BPS) during system disturbances.
At Keentel Engineering, we are actively supporting generator owners, developers, and asset managers as they navigate the technical, modeling, protection, and compliance implications of PRC-029-1. Our team has developed a structured IBR Plant Ride-Through Design Evaluation Framework to help clients demonstrate compliance while improving overall grid reliability.
Understanding PRC-029-1: Ride-Through Redefined
PRC-029-1 establishes minimum mandatory ride-through criteria for both voltage and frequency excursions, requiring IBRs to remain connected and operational during defined grid disturbance profiles.
This standard addresses a well-documented reliability gap highlighted in multiple NERC disturbance and event analysis reports, where premature tripping of IBRs during normally cleared faults contributed to system instability. As inverter-based generation penetration continues to increase, ensuring consistent ride-through performance is essential to maintaining BPS reliability.
Scope of Applicability
PRC-029-1 applies to both BES and registered Category 2 IBRs:
BES IBRs
- Gross nameplate capacity > 75 MVA
- Connected at ≥ 100 kV
Non-BES (Category 2) IBRs
- Gross nameplate capacity ≥ 20 MVA
- Connected at ≥ 60 kV
While both categories are subject to the same technical ride-through requirements, their implementation timelines differ, which has important planning implications for asset owners.
Requirements Overview
PRC-029-1 consists of four primary requirements:
R1–R3: Design and Operational Performance
These requirements define how IBR facilities must be designed, configured, and operated to successfully ride through the voltage and frequency conditions specified in the PRC-029 performance curves.
Design compliance includes:
- Configuring inverter controls, protection systems, relays, and balance-of-plant protections
- Verifying power plant controller (PPC) and inverter operating modes
- Confirming that dynamic models accurately reflect as-left configurations
- Performing simulation-based ride-through studies to demonstrate compliance under required disturbance profiles
Requirement R4 allows Generator Owners (GOs) to request limited exemptions for existing IBRs that cannot fully meet PRC-029-1 due to hardware-based limitations.
Software or control-based upgrades are expected where feasible; exemptions are primarily intended for non-modifiable equipment constraints.
Implementation Timeline
For BES IBRs
- Design Requirements (R1–R3): October 1, 2026
- Operational Requirements: After PRC-028-1–compliant disturbance monitoring is in service
- R4 Exemption Documentation Due: October 1, 2026
For Non-BES IBRs
- Design Requirements (R1–R3): January 1, 2027, or the standard’s effective date (whichever is later)
- Operational Requirements: Triggered once PRC-028-1 monitoring is operational
- R4 Exemption Documentation Due: January 1, 2027, or the effective date
Note: The effective date of PRC-029-1 is expected to be October 1, 2026, defined as the first day of the first calendar quarter 12 months following FERC approval. Final confirmation should be verified through official NERC publications.
Legacy Equipment and Exemption Requests
A 12-month exemption request window begins on the standard’s effective date. Generator Owners of existing IBRs placed in service prior to October 1, 2026 may submit exemption requests for qualifying hardware-based limitations under Requirement R4.
All exemption requests must be supported by clear, defensible technical documentation, demonstrating why compliance cannot be achieved through reasonable upgrades or configuration changes.
FERC Directives to NERC
In Order 909, FERC directed NERC to expand acceptable forms of technical evidence beyond OEM-provided damage curves. Acceptable documentation may include:
- Inverter manufacturer certifications
- Commissioning or factory acceptance test data
- Independent engineering analyses demonstrating infeasibility of compliance
FERC also instructed NERC to consider exemptions for:
- HVDC-connected IBRs with inherent thermal or design-based ride-through constraints (e.g., offshore wind with chopper circuits)
- Long-lead-time projects already under development prior to the effective date
If hardware modifications are later implemented after an exemption is granted, Generator Owners must notify their Planning Coordinator, Transmission Planner, Reliability Coordinator, and Transmission Operator within 90 days, after which full compliance with R1–R3 is required.
Compliance Planning: Key Considerations
With implementation timelines approaching, IBR owners should begin PRC-029-1 readiness activities now, including:
diness activities now, including:
- Reviewing project designs and as-left inverter, relay, and PPC settings against PRC-029-1 performance curves
- Coordinating with OEMs to obtain capability documentation and identify potential exemption needs
- Conducting PRC-029 design evaluations, including protection and control reviews and simulation-based assessments
- Deploying PRC-028-1 disturbance monitoring equipment to support operational compliance
- Assessing legacy assets for upgrade feasibility and preparing exemption documentation where necessary
Looking Ahead
FERC has directed NERC to submit a report 18 months after the close of the exemption window detailing the number, nature, and system-wide impact of granted exemptions. This underscores increasing regulatory scrutiny of IBR performance and reinforces the long-term expectation that all grid-connected resources provide essential reliability services, including robust fault ride-through capability.
How Keentel Engineering Can Hel
Keentel Engineering supports clients throughout the entire PRC-029-1 compliance lifecycle, including:
- Development of PRC-029-1 compliance procedures
- Compliance rollout and implementation planning
- Review of as-left protection, control, and inverter settings
- Coordination with inverter and PPC OEMs
- Simulation-based design evaluations using PSCAD, PSS®E, PSLF, DigSILENT PowerFactory, and EMT tools
- Preparation of R4 exemption technical documentation
- PRC-028-1 disturbance monitoring gap analyses
- Support for PRC-030 event analysis following ride-through failures
To learn how PRC-029-1 may impact your existing fleet or upcoming projects, contact Keentel Engineering or visit our website to request support.
Reference Materials
- FERC Order 909 – PRC-029-1 Final Rule (Docket RM25-3-000)
- NERC PRC-029-1 Reliability Standard
- NERC PRC-029-1 Implementation Plan
Contact us

About the Author:
Sonny Patel P.E. EC
IEEE Senior Member
In 1995, Sandip (Sonny) R. Patel earned his Electrical Engineering degree from the University of Illinois, specializing in Electrical Engineering . But degrees don’t build legacies—action does. For three decades, he’s been shaping the future of engineering, not just as a licensed Professional Engineer across multiple states (Florida, California, New York, West Virginia, and Minnesota), but as a doer. A builder. A leader. Not just an engineer. A Licensed Electrical Contractor in Florida with an Unlimited EC license. Not just an executive. The founder and CEO of KEENTEL LLC—where expertise meets execution. Three decades. Multiple states. Endless impact.
Services

Let's Discuss Your Project
Let's book a call to discuss your electrical engineering project that we can help you with.

About the Author:
Sonny Patel P.E. EC
IEEE Senior Member
In 1995, Sandip (Sonny) R. Patel earned his Electrical Engineering degree from the University of Illinois, specializing in Electrical Engineering . But degrees don’t build legacies—action does. For three decades, he’s been shaping the future of engineering, not just as a licensed Professional Engineer across multiple states (Florida, California, New York, West Virginia, and Minnesota), but as a doer. A builder. A leader. Not just an engineer. A Licensed Electrical Contractor in Florida with an Unlimited EC license. Not just an executive. The founder and CEO of KEENTEL LLC—where expertise meets execution. Three decades. Multiple states. Endless impact.
Leave a Comment
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.