A Coordinated Electric System Interconnection Review—the utility’s deep-dive on technical and cost impacts of your project.
Symmetrical Components Is a Powerful Technique Used in Electrical Engineering
March 1, 2023 | Blog
Symmetrical Components
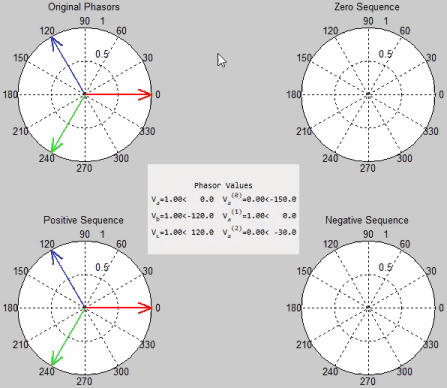
Symmetrical components is a powerful analytical method in electrical engineering used to diagnose and understand unbalanced conditions in three-phase power systems. In a perfectly balanced three-phase system, voltages and currents have equal magnitudes and are separated by 120 degrees. But in the real world, imbalances occur due to faults, unbalanced loads, or network asymmetry.
This method allows engineers to transform an unbalanced three-phase system into three independent and balanced sets of components, simplifying analysis and improving fault detection.
Three Key Components
1️⃣ Positive Sequence Component
The positive sequence component represents the balanced part of the system and behaves identically to the ideal three-phase source. It contributes to normal operation and is denoted with the subscript “1”.
2️⃣ Negative Sequence Component
The negative sequence component represents imbalances where voltages and currents have equal magnitude but are out of phase by 120 degrees in the opposite sequence. It is often caused by asymmetrical loads or faults, and can lead to overheating in rotating machines. It’s denoted with the subscript “2”.
3️⃣ Zero Sequence Component
The zero sequence component is used to represent ground faults or neutral imbalances where all three-phase voltages or currents are in-phase. It’s typically a key indicator of earth faults and is denoted by subscript “0”.
Engineers often rely on these components for fault analysis and protection coordination. Learn how we support this in our Power System Studies
Why Use Symmetrical Components?
Breaking down the system using symmetrical component analysis offers several benefits:
- Simplifies complex fault analysis under unbalanced conditions
- Improves the accuracy of relay protection schemes
- Enables detailed modeling of short circuits, open conductor faults, and line-to-ground imbalances
- Helps predict and mitigate system performance issues
This method is especially important when designing NERC-compliant protection systems. See our NERC Compliance Services for more.
Applications in Protective Relaying
Symmetrical components play a crucial role in protective relaying schemes. During fault events:
- Relays analyze the sequence components of fault currents
- Algorithms determine fault type and location
- The system triggers protective actions like breaker tripping or reconfiguration
This allows for fast, selective, and accurate response during critical events.
Conclusion of Symmetrical Components
Symmetrical component theory provides a structured way to analyze unbalanced power systems. By isolating the positive, negative, and zero sequence elements, electrical engineers can design more robust and efficient systems, improving grid reliability, equipment protection, and regulatory compliance.
Want to explore fault modeling using symmetrical components? Contact us to learn how we can simulate and optimize your system.
Improve Fault Detection and Grid Modeling Accuracy
At Keentel Engineering, we specialize in advanced modeling, fault simulations, and relay coordination using symmetrical component analysis. Whether it’s for substation protection or DER interconnection — we’ve got you covered.

About the Author:
Sonny Patel P.E. EC
IEEE Senior Member
In 1995, Sandip (Sonny) R. Patel earned his Electrical Engineering degree from the University of Illinois, specializing in Electrical Engineering . But degrees don’t build legacies—action does. For three decades, he’s been shaping the future of engineering, not just as a licensed Professional Engineer across multiple states (Florida, California, New York, West Virginia, and Minnesota), but as a doer. A builder. A leader. Not just an engineer. A Licensed Electrical Contractor in Florida with an Unlimited EC license. Not just an executive. The founder and CEO of KEENTEL LLC—where expertise meets execution. Three decades. Multiple states. Endless impact.
Services

Let's Discuss Your Project
Let's book a call to discuss your electrical engineering project that we can help you with.

About the Author:
Sonny Patel P.E. EC
IEEE Senior Member
In 1995, Sandip (Sonny) R. Patel earned his Electrical Engineering degree from the University of Illinois, specializing in Electrical Engineering . But degrees don’t build legacies—action does. For three decades, he’s been shaping the future of engineering, not just as a licensed Professional Engineer across multiple states (Florida, California, New York, West Virginia, and Minnesota), but as a doer. A builder. A leader. Not just an engineer. A Licensed Electrical Contractor in Florida with an Unlimited EC license. Not just an executive. The founder and CEO of KEENTEL LLC—where expertise meets execution. Three decades. Multiple states. Endless impact.
Leave a Comment
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.